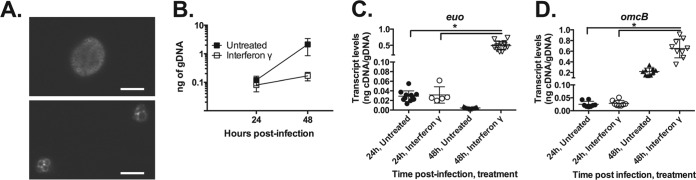
FIG 1.
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ) induces a highly reproducible persistent phenotype in C. pneumoniae. (A) Characteristic immunofluorescent images of C. pneumoniae cells from untreated or IFN-γ-treated cultures. HEp-2 cells were infected with C. pneumoniae and treated or not with IFN-γ. At 48 h postinfection, infected cells were fixed and stained for the major outer membrane protein. IFN-γ-induced persistence results in smaller inclusions containing aberrantly enlarged RB forms. (B) Quantification of C. pneumoniae genomic DNA (gDNA) by qPCR from untreated (solid symbols) and IFN-γ-treated (open symbols) cultures at 24 and 48 h postinfection. (C and D) Quantification of C. pneumoniae euo (C) and omcB (D) transcript levels from untreated and IFN-γ-treated cultures at 24 and 48 h postinfection. Individual data points (themselves averages from three measurements) are from all technical and biological replicates from all experiments (n = 7, except 24-hpi IFN-γ, where n = 4). *, P ≤ 0.05 for 48-hpi IFN-γ versus 24-hpi IFN-γ.