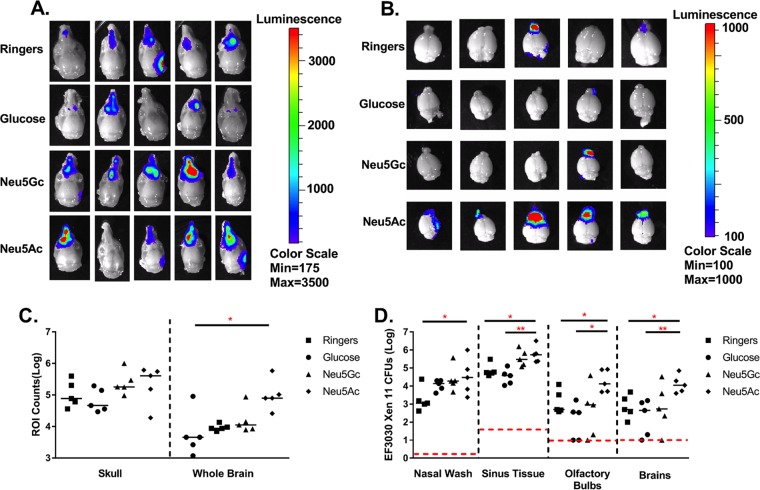
FIG 3.
Treatment with N-acetylneuraminic acid but not N-glycolylneuraminic acid leads to increased invasion into the brain. (A and B) Six- to eight-week-old BALB/cByJ were intranasally infected with 107 CFU of EF3030 Xen 11 without anesthesia. After 24 h, mice were treated with lactated Ringer's solution, 1 mg of N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac), 1 mg of N-glycolylneuraminic acid (Neu5Gc), or 1 mg of glucose (GLU). Animals were then perfused, and skinned heads (A) and brains (B) were imaged at 4 days postinfection. (C) An ROI was identified, and light emission was measured (counts) minus the background. The whole brain refers to brain and olfactory bulbs. (D) CFU from tissue homogenates enumerated from infected animals. The dashed line indicates the minimum level of detection, and the solid bar represents the median. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA (C) and a Mann-Whitney rank sum test (D) (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 [indicating significant differences between populations]).