FIG 7.
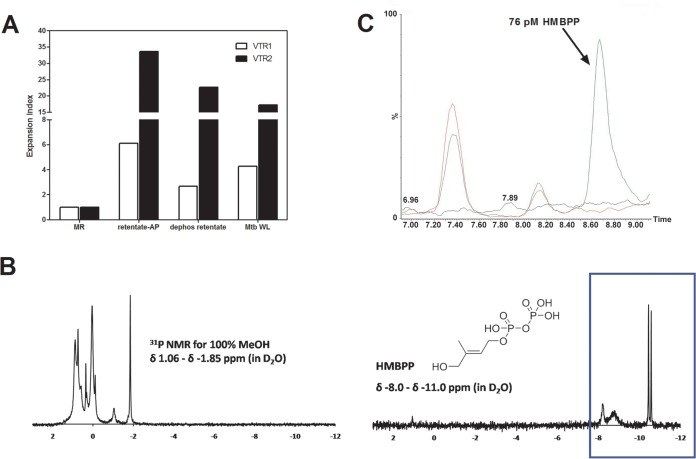
The novel mycobacterial stimulatory molecules are distinct from phosphoantigens of H37Rv. Total lipid (10:10:3) was dried via rotary evaporation and resuspended in chloroform-methanol (2:1). The suspension was transferred to glass tubes and centrifuged. The chloroform-methanol-insoluble material was resuspended in water and filtered through an Amicon Ultra (MWCO, 3,000) iteratively to obtained both retentate and eluate substrates for alkaline phosphatase (AP) treatments and dephosphorylated treatments. All the treated fractions were tested for the ability to expand γ9δ2 T cells. (A) EI of γδ T cells. Active fractions of M. tuberculosis, when treated with alkaline phosphatase to hydrolyze phosphoryl esters, still retain the ability to expand γδ T cells. (B) Difference in 31P NMR chemical shifts of 100% MeOH fraction and commercial HMBPP (blue box). (C) Overlay of injection series for solvent only (black line), mGLP only (red line), and mGLP spiked with 76 pM HMBPP (green line). Note the absence of HMBPP (to a limit of detection of 19 pM), which resolves between the retention time of 8.55 and 8.95 min, in mGLP, even when 2.63 μg of sample (green line) is injected onto the MS instrument. Minor peaks represent other mGLP products, resolving separately from HMBPP, during chromatography of mGLP. The x axis represents retention time (minutes); the y axis is normalized to percent relative abundance of signal in each sample based on the total peak area for 76 pM HMBPP.