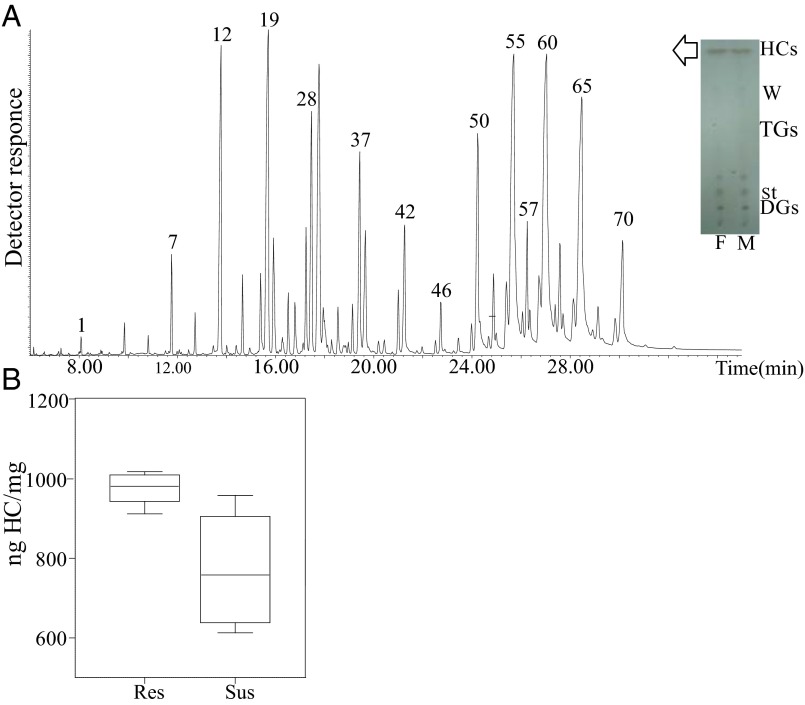
Fig. 2.
Analysis of adult An. gambiae CHCs. (A) Representative total ion current (TIC) profile of An. gambiae HCs. Numbers indicating major HC peaks correspond to peak numbers from Dataset S1. (Inset) TLC for the separation of lipid species. Cuticular lipids from male (M) and female (F) mosquitoes were extracted by hexane and subsequently separated on 2D TLC. HCs are the major lipid species, compared with waxes (W), sterols (St), diglycerides (DGs), or triglycerides (TGs). First dimension of TLC: hexane; second dimension: hexane/diethyl ether/acetic acid. Visualization of lipids was performed after spraying the plates with 5% sulfuric acid in 95% ethanol, and charring at 180–200 °C for 20 min. (B) Comparison of CHCs in resistant (Res) and susceptible (Sus) females. The CHCs derived from resistant and susceptible adult (12- to 14-d-old) female mosquitoes were quantified by GC-MS/FID (20 insects pet vial) and were found to be significantly higher in resistant than in susceptible mosquitoes (980.5 ± 18.6 ng CHCs/mg of mosquito and 757.5 ± 72.5 ng CHCs/mg of mosquito, respectively). The box plots show the 25th and 75th percentile; the mean is shown as a black line within the box; error bars correspond to the 10th and 90th percentiles.