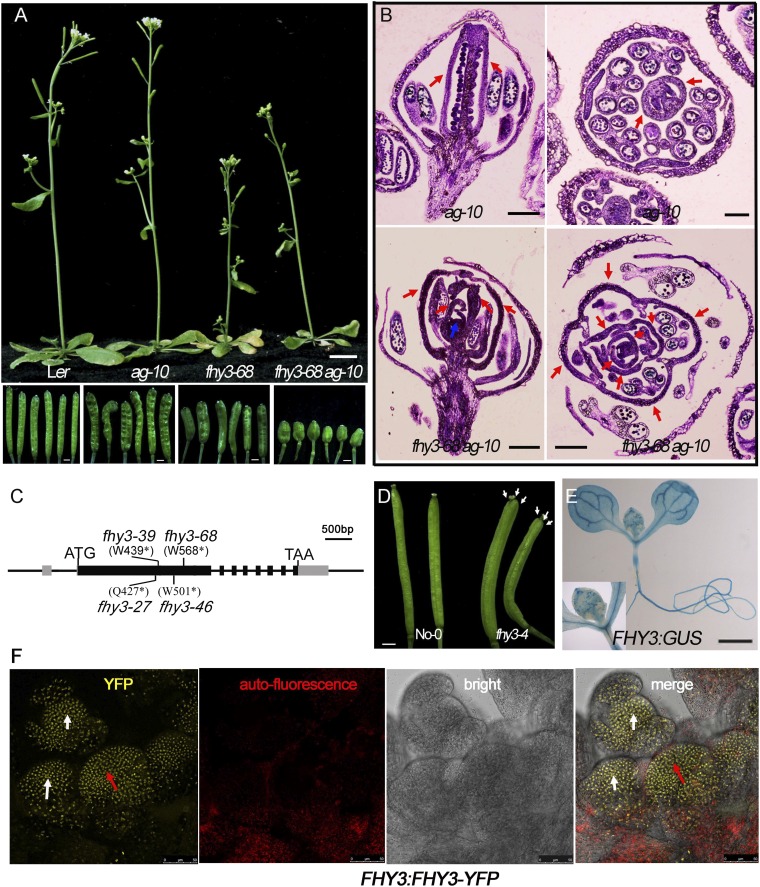
Fig. S1.
Various FHY3 mutants and their phenotypes in the wild-type and ag-10 backgrounds. (A) Phenotype of indicated plants (Upper) and siliques (Lower). All siliques of fhy3-68 ag-10 plant are bulged and short. (B) Longitudinal (Left) and transversal (Right) sections of indicated plants siliques. Although ag-10 produced two fused carpels (red arrows), the indeterminate floral meristem (blue arrow) of fhy3-68 ag-10 continued to generate additional organs inside the carpels (red arrows). (C) Gene diagram of FHY3 and the locations of mutations in the various fhy3 mutants used in this work. ATG and TAG correspond to the start and stop codons, respectively. The gray and black rectangles represent the 5′ or 3′ UTRs and coding regions, respectively. The black lines represent introns or intergenic regions. All mutations are nonsense mutations. (Scale bar, 500 bp.) (D) Siliques of No-0 (Left) and fhy3-4 (Right) plants. fhy3-4 siliques had three fused carpels (marked by white arrows). (E) Tissue-specific expression of FHY3 using FHY3:GUS transgenic plant. FHY3 is universally expressed in the seedling and SAM (Inset). (F) FHY3-YFP signal in the SAM and FM of FHY3:FHY3-YFP. Red arrows indicate YFP signal in SAM and white arrows indicate YFP signal in FM. [Scale bars: 1 cm in A (Upper) and 1 mm (Lower); 200 µm in B; 1 mm in D and E; and 50 µm in F.]