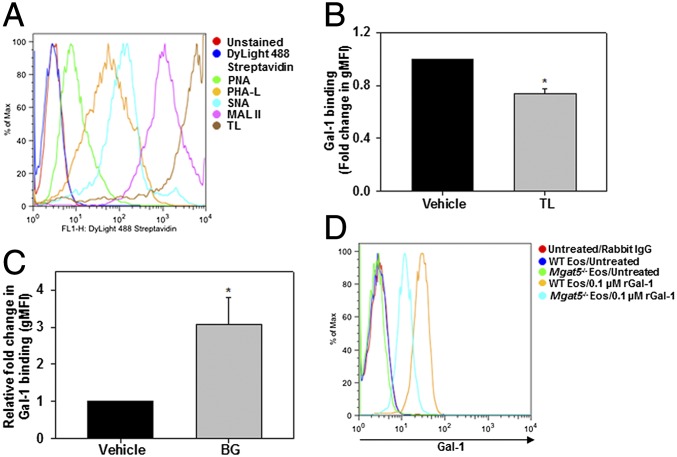
Fig. 3.
Gal-1 binding to eosinophil-expressed glycans. (A) Glycophenotype analysis of BM eosinophils. Cells were incubated with specific plant lectins followed by streptavidin-conjugated DyLight 488 and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (B) Gal-1 binding to eosinophils pretreated with TL or vehicle (PBS) examined by flow cytometry with Gal-1 antibody. gMFI, geometric mean fluorescence intensity. (C) Role of O-glycans in Gal-1 binding. Eosinophils cultured in medium containing BG (2 mM) or vehicle (DMSO) were treated with rGal-1 and examined for Gal-1 binding. (D) Requirement of complex branched N-glycans for Gal-1 binding. WT and Mgat5−/− eosinophils (nonpermeabilized) were treated with rGal-1 and examined for Gal-1 binding. Data in A and D are representative of three independent experiments with eosinophils from different mice. Combined data (mean ± SEM) of four experiments are shown in B and C. *P < 0.01 in B and *P < 0.03 in C versus vehicle-treated cells.