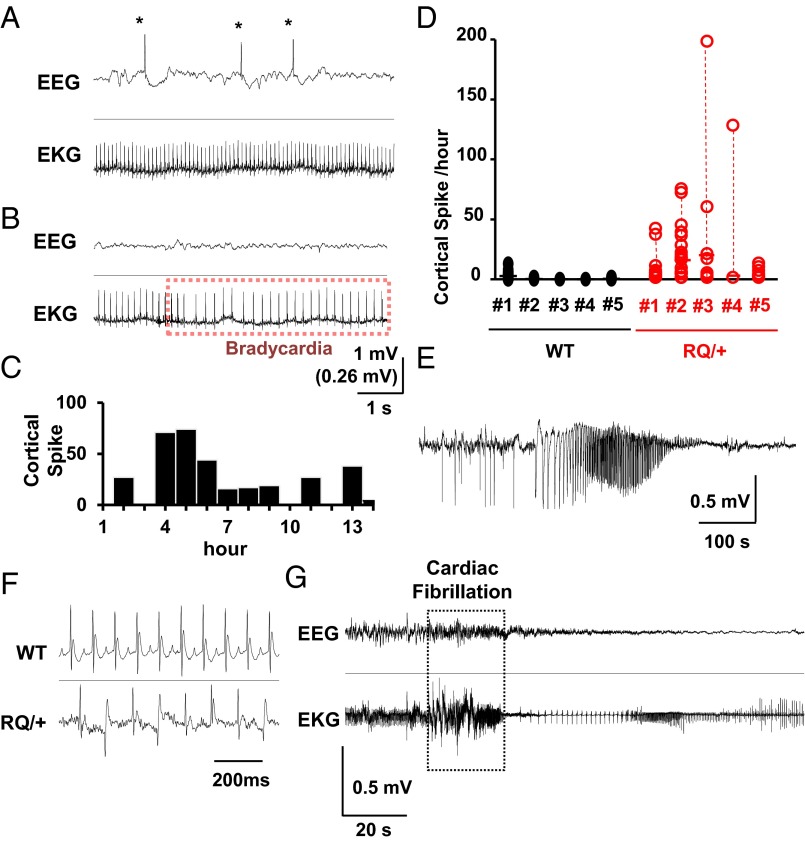
Fig. 1.
In vivo simultaneous EEG and EKG monitoring of awake RQ (R176Q/+) mutant and WT male mice (P30–50, n = 5 each) revealed resting abnormalities in brain and cardiac rhythms. (A and B) Representative traces of cortical spikes (*) with normal EKG (A) and a brief episode of bradycardia with normal EEG activity (B). (C) Histogram of spike distribution from a RQ mouse showing the large variability in EEG spike occurrence. (D) Summary of spike frequency from five RQ mutant and WT animals. Each data point shows numbers of spikes in 1-h bins. (E) EEG tracing showing an example of a spontaneous convulsive seizure in a RQ mutant mouse. (F) EKG recordings from WT (Top) and RQ mutant mice (Bottom) 10 min after caffeine injection (100 mg/kg, i.p.). Cardiac arrhythmias were seen in RQ mutant but not WT mice. (G) Caffeine injection led to cardiac fibrillation and arrest in RQ mutant mice. No abnormal EEG discharges were seen during caffeine-induced lethal cardiac arrhythmias.