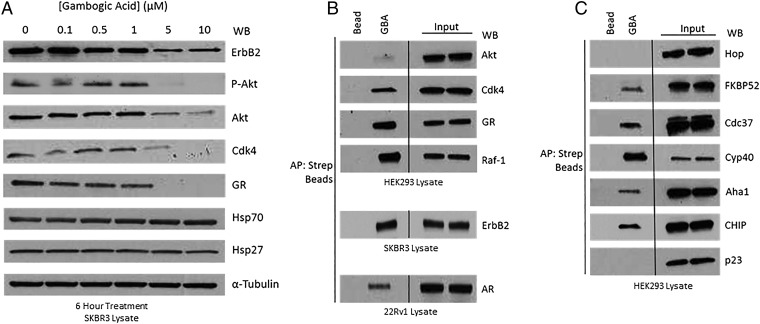
Fig. 2.
Gambogic acid promotes degradation of Hsp90-dependent clients and demonstrates a unique client and cochaperone binding profile. (A) SKBR3 cells were treated with GBA for 6 h at increasing concentrations. GBA induced potent, dose-dependent degradation of several endogenous Hsp90 client proteins, although not significantly impacting expression of either of the cytoprotective chaperones Hsp70 and Hsp27. (B and C) Hsp90β–client and Hsp90β–cochaperone complexes were isolated from HEK293, SKBR3, and 22Rv1 cell lysates with Bio-GBA and streptavidin beads. (B) Bio-GBA is able to pull down Hsp90 complexed to several endogenous client proteins, unlike most classic NTD-targeted Hsp90 inhibitors. (C) Bio-GBA recognizes Hsp90 in complex with multiple cochaperones recognizing distinct Hsp90 conformational states.