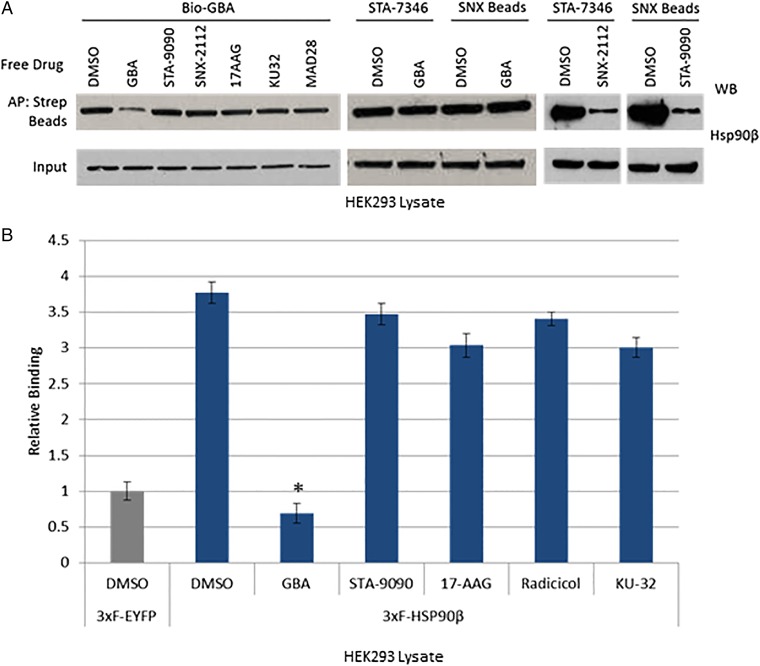
Fig. 3.
Gambogic acid binds at a site distinct from NTD and CTD Hsp90 inhibitors. (A) HEK293 cells were lysed and lysates were treated with various Hsp90 inhibitors (10 μM). Bio-GBA and streptavidin beads were then added to isolate Hsp90β. Only unlabeled GBA was able to compete with Bio-GBA for binding. Conversely, HEK293 lysate was also incubated with free GBA and pulled down with STA-7346– or SNX-2112–conjugated drug beads. GBA did not block binding of these NTD-targeted inhibitors. As a positive control, STA-9090 (ganetespib) was added to lysate followed by Hsp90 pulldown with SNX-2112–conjugated beads and competitive binding inhibition was observed. Similar competitive binding inhibition was seen when SNX-2112 was added to lysate followed by Hsp90 pulldown with STA-7346. (B) LUMIER analysis of drug competition confirmed that no NTD- or CTD-targeted inhibitors compete with GBA for binding to Hsp90β. Error bars represent SDs. *P < 0.05.