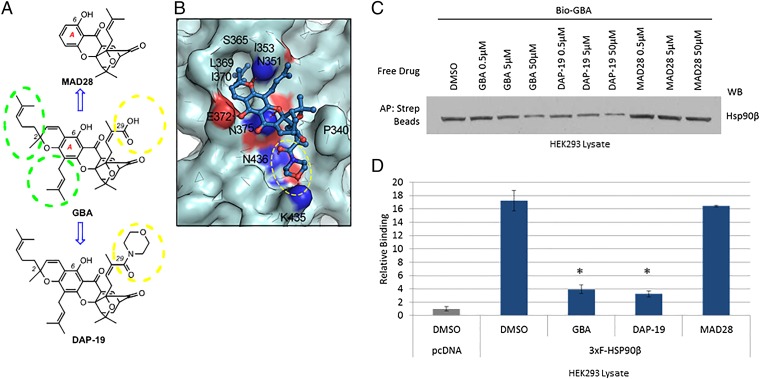
Fig. 6.
Model-based structural modifications of GBA increase or decrease binding to Hsp90β. (A) Drug schematic indicates key structural differences between GBA, MAD28, and DAP-19. Hydrophobic side chains at the periphery of the A ring of GBA are marked with green dashed circles. Substituents at the C29 center are marked with a yellow dashed circle. (B) Predicted binding mode of DAP-19 (shown in blue stick representation) against Hsp90β (shown in pale cyan). The morpholine amide group at C29 is marked with a yellow dashed circle. (C) HEK293 cells were lysed and treated with unlabeled GBA, DAP-19, or MAD28 at various concentrations. Endogenous Hsp90β was then isolated from cell lysates with Bio-GBA and streptavidin beads. Compared with unlabeled GBA, DAP-19 more effectively blocked Hsp90β binding to Bio-GBA, whereas MAD28 was less effective. (D) Data obtained from LUMIER analysis are consistent with the results obtained by Western blot (C). Error bars represent SDs. *P < 0.05 relative to DMSO.