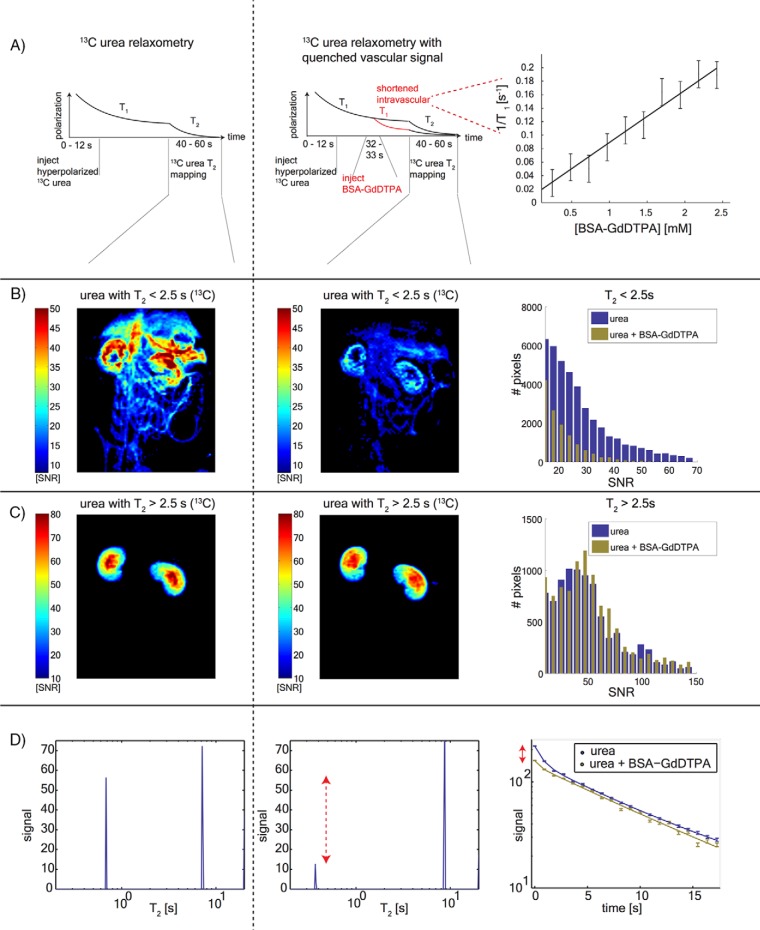
Figure 3.
[13C,15N2]urea T2 relaxometry after quenching the vascular signal. Timeline of the substrate injections and imaging (A). The left column shows images from the control experiment, and the center column shows the post-BSA-GdDTPA images. The [13C,15N2]urea T1/BSA-GdDTPA relaxivity curve is shown on the right. [13C,15N2]urea signal outside of the kidneys has T2 of <2.5 seconds, which is strongly attenuated by BSA-GdDTPA (B). Pixel distributions from 4 animals are shown on the right. The long T2 urea signal component is confined to the kidneys and is unaffected by the BSA-GdDTPA chaser (C). Pixel distributions from 4 animals are shown on the right. T2 distributions of single pixels selected from the center of the kidneys are showing this short T2 signal attenuation (red arrow) (D). Single-pixel T2 decay curves (corresponding to the distributions in the left and center panels).