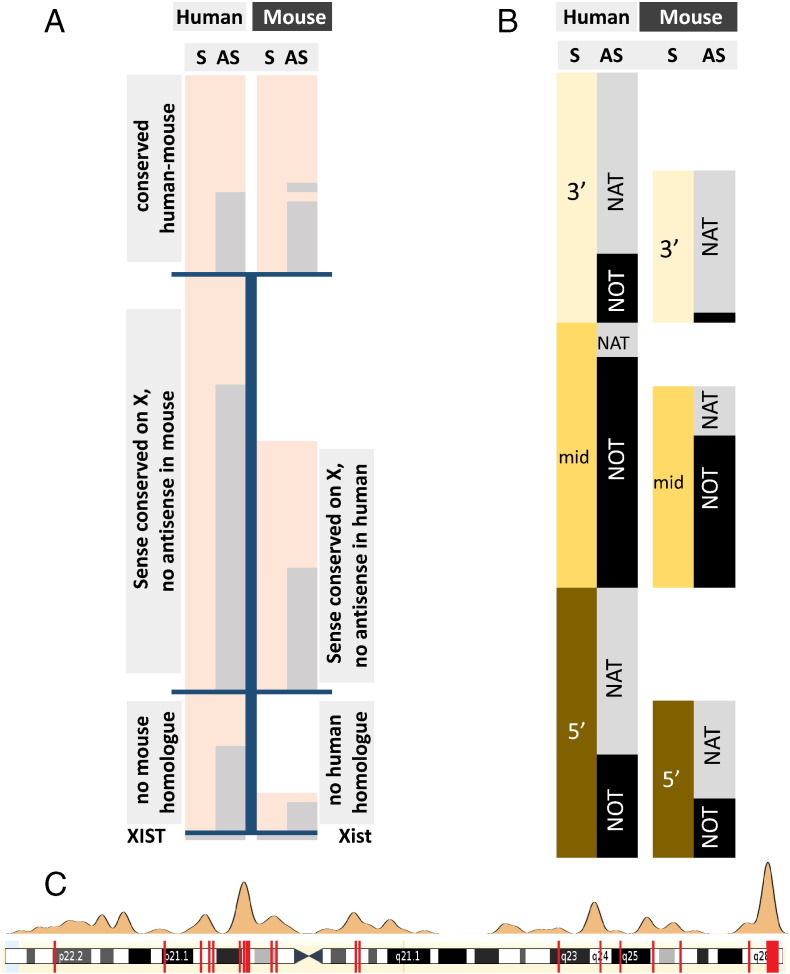
Fig. 5.
Natural antisense transcripts on X chromosomes of human and mouse. A) Phylogenetic conservation of sense and antisense transcripts. Top panel, conserved bi-directional locus between human and mouse; middle panel, locus conserved but no antisense transcript in the other species; homologue in the other species. Light peach indicates protein coding potential, S = sense, AS = antisense. The nature of synteny is described in the grey boxes. B) Comparison of the genomic arrangement of bi-directionally transcribed genes on the X chromosome of human and mouse. 3′, mid and 5′ indicates the position of complementarity between sense and antisense transcript. NAT stands for an antisense transcript with complementarity to the sense RNA; NOT indicates a non-overlapping configuration. C) Natural antisense transcripts in regions that escape X chromosome inactivation. Upper panel indicates areas with relaxed inactivation, the red bars on the lower panel depict the bi-directionally transcribed human genes.