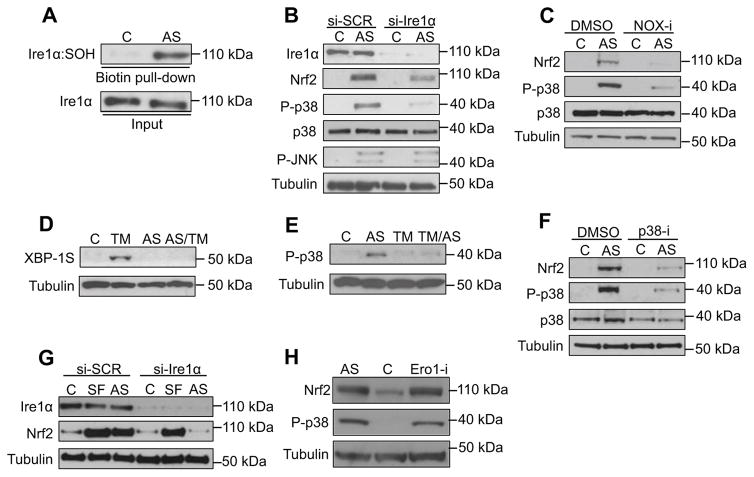
Figure 5. Evolutionary conservation of the IRE-1 antioxidant response function.
(A) Human Ire1α senses ROS. Ire1α sulfenylation was assessed in HepG2 cells following AS (30 min) treatment. (B) Ire1α is required for the p38 and Nrf2 response to AS-induced ROS. Levels of Nrf2 accumulation, p38 phosphorylation and activation were assayed in HepG2 cells treated with either control siRNA (si-SCR) or Ire1α siRNA (si-Ire1α) following AS (30 min) treatment. (C) NOX-derived ROS activate the p38/Nrf2 pathway. Levels of Nrf2 and p38 activation were determined in HepG2 cells treated with AS (30 min) in the absence or presence of the pan-NOX inhibitor VAS2870 (NOX-i)(1 hr). (D–E) Ire1α senses ROS and ER stress in a mutually exclusive manner. HepG2 cells were treated with AS (30 min) prior to TM (5 hr) treatment, with Xbp1S protein assayed by immunoblot (D). Levels of active p38 were determined in HepG2 cells following treatment with AS (30 min) alone, TM (5 hr) alone or pretreatment with TM prior to acute AS exposure (E). (F) Nrf2 activation by AS requires p38. HepG2 cells were treated with vehicle control or the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (p38-i) (2 hr) prior to AS (30 min). (G) Ire1α regulates Nrf2 independently of Keap1. HepG2 cells treated with either control siRNA (si-SCR) or Ire1α siRNA (si-Ire1α) were exposed to either the Keap1 inhibitor sulforaphane (SF) (30 min) or AS (30 min). (H) Activation of the p38/Nrf2 response by ER-derived ROS. Treatment of HepG2 cells with Ero1 inhibitor II (2 hr) activated p38 and Nrf2 comparably to AS. See also Figure S5.