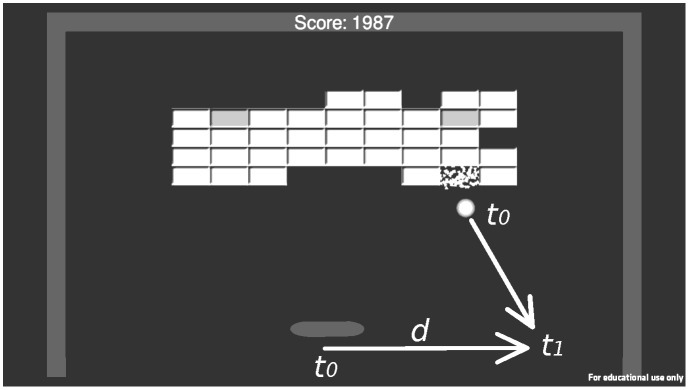
Fig 2. Breakout-EMG.
Screenshot of Breakout-EMG showing an example of a terminal ball drop. The distance that the ball needed to move was calculated by determining the interval from the point at which the ball began to drop down towards the ground (t0) and the point at which the ball got to the height (y-position) of the paddle (t1). The required distance was the difference in position of the paddle at t0 and the position of the ball at t1. The required distance was correlated to the observed net EMG signal (see text for details).