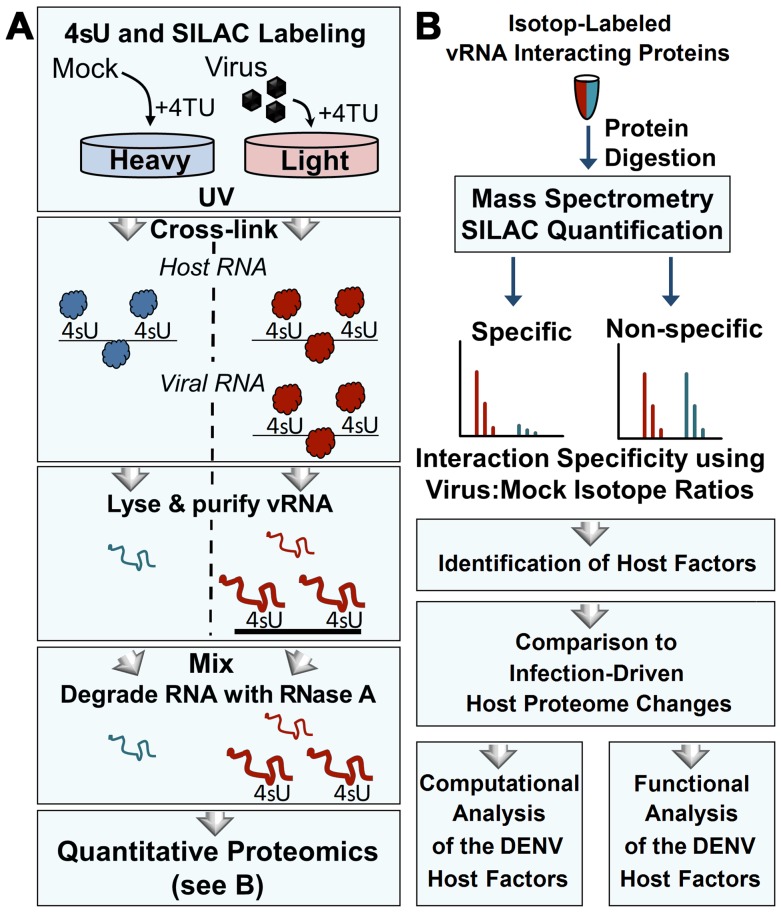
Fig 1. Isolation and identification of cellular proteins that associate with DENV RNA by qTUX-MS.
(A) Diagram of the qTUX-MS method and SILAC labelling. Huh7.5UPRT cells labelled with the ‘light’ (red) or ‘heavy’ (blue) amino acids are infected with DENV or treated with mock, respectively, in the presence of 4TU. 4sU is incorporated into cellular and DENV RNAs and proteins are UV cross-linked to the contacting thio-containing RNA (represented as either balls to indicate native conformation or curved lines to indicate denatured proteins) in living cells at 28 hpi prior to cell lysis under denaturing conditions. Viral ribonucleoprotein complexes were isolated using DNA molecules complementary to DENV RNA bound to magnetic beads, the RNA was degraded with RNase A and the proteins were identified by mass spectrometry. (B) Workflow for quantitative proteomic analysis of RNA-bound host factors isolated in (A). Isolated proteins were mixed between mock and virus-infected samples, digested into peptides, and analysed by mass spectrometry. Relative ‘light’ and ‘heavy’ peptide abundances were quantified to determine the specificity of interaction. Host factor candidates were identified and subjected to functional validation.