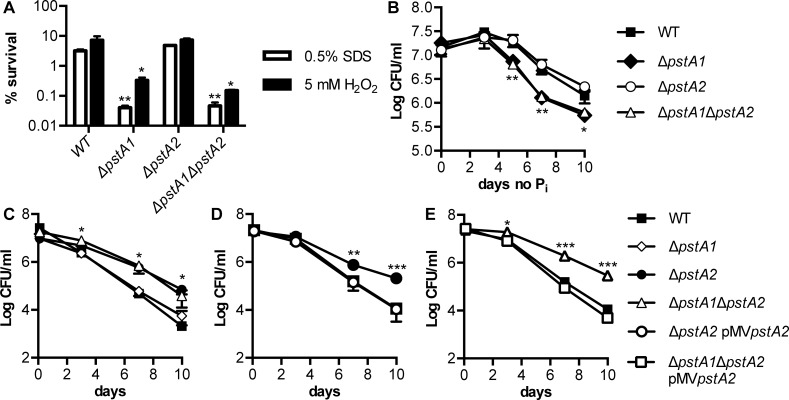
Fig 5. Deletion of pstA2 causes increased resistance to acidified medium.
M. tuberculosis WT, ΔpstA1, ΔpstA2, ΔpstA1ΔpstA2, ΔpstA2 pMVpstA2 and ΔpstA1ΔpstA2 pMVpstA2 strains were grown to mid-exponential phase in Pi-rich 7H9 medium and then subjected to stress conditions, as indicated. Bacterial CFU were enumerated by plating serially diluted cultures on 7H10 agar and incubating for 3 to 4 weeks at 37°C. Percent survival was calculated as (CFU poststress)/(CFU pre-stress)x100. Data shown are means ± standard deviations of three independent cultures from one experiment, and are representative of at least three independent experiments. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between the deletion mutant and WT control for panels A-C or between the deletion mutant and both the WT and complemented strains for panels D and E: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0005. (A) Cell wall stress (sodium dodecyl sulfate, SDS) and reactive oxygen stress (hydrogen peroxide, H2O2). Either 0.5% SDS or 5 mM H2O2 was added to each culture. CFU were enumerated at 0 and 24 hours and percent survival was calculated. (B) Pi starvation. Bacteria were shifted to Pi-free medium and CFU were enumerated at 0, 3, 5, 7, and 10 days. (C-E) Acidic pH stress. Bacteria were shifted to acidified 7H9 medium pH 4.5 containing 0.1% Tween-80 and CFU were enumerated at 0, 3, 7, and 10 days.