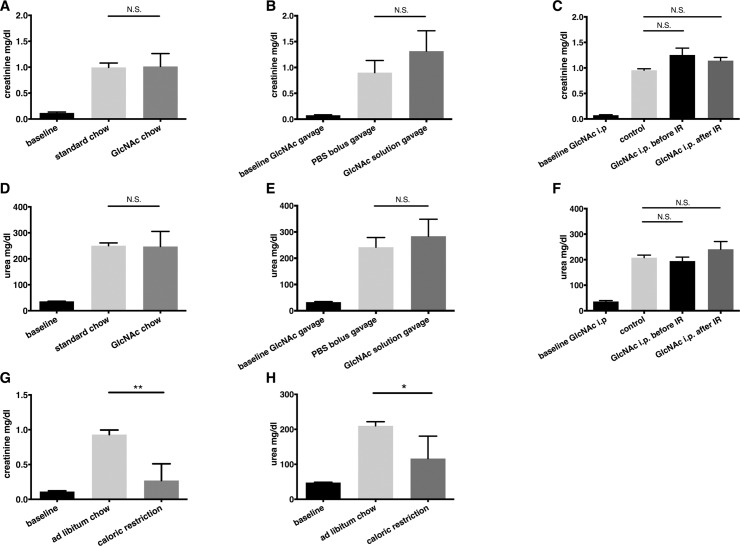
Fig 4. Kidney failure 24 hours after ischemia-reperfusion injury in preconditioned and control animals.
Creatinine and urea values after unilateral nephrectomy followed by 40 minutes of ischemia and 24 hours of reperfusion (IR) of the contralateral kidney. Different dosing regimens for GlcNAc were used. A) and D) Mice were kept on a four-week ad libitum diet enriched with 0.5% GlcNAc (n = 17) or received standard chow ad libitum (n = 15). B) and E) Mice received a 250 μl PBS twice, 24 and 2 hours before IR by gavage (n = 5). In the verum group PBS contained 10% GlcNAc (n = 10). C) and F) Verum mice were injected 20 mg GlcNAc in PBS either one hour before surgery i.p (n = 3) or immediately at the end of ischemia at the beginning of reperfusion (n = 4) directly into the abdominal cavity. Baselines represent control animals from Fig 1A and 1B without ischemia-reperfusion injury A) and D) for untreated animals (n = 5), B) and E) for mice after gavage of 10% GlcNAc solution (n = 6) and C) and F) for mice after i.p. injection of 10 mg GlcNAc (n = 5). After four weeks of caloric restriction (n = 4) with standard chow mice are protected against ischemia-reperfusion damage compared to controls having ad libitum access to standard chow (n = 5) (G+H).