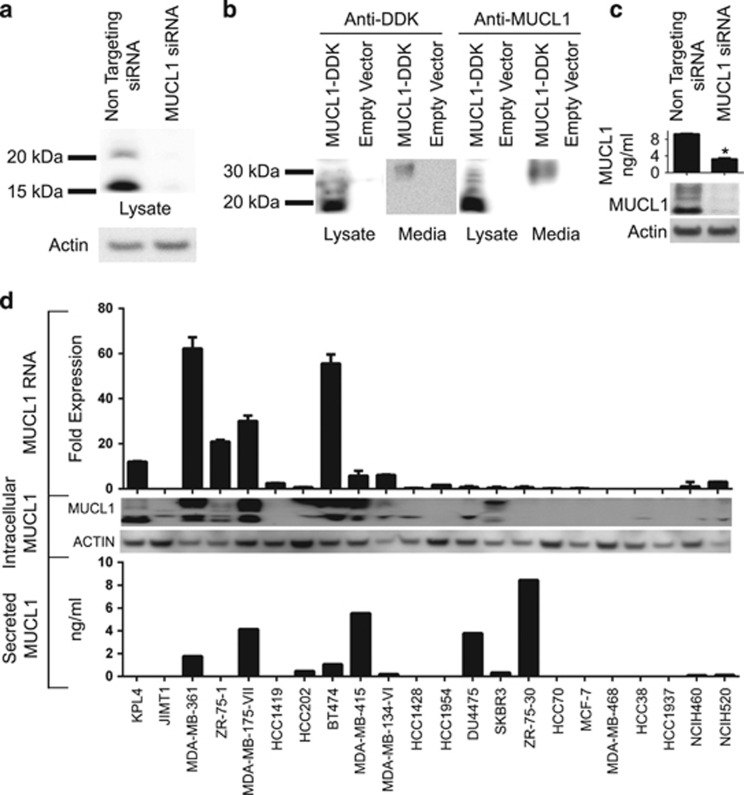
Figure 3.
MUCL1 RNA and protein expression was examined in a panel of breast and lung cancer cell lines as described in Table 1. (a) KPL4 cells were transiently transfected with either NT siRNA or MUCL1 siRNA for 48 h. Cell lysates were probed using a rabbit polyclonal anti-MUCL1 antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control. (b) HEK-293 cells were transfected with a DDK-tagged MUCL1 expression vector or empty vector. After 48 h, cell lysates and culture supernatant were immunoblotted using anti-DDK and anti-MUCL1 antibodies. (c) MDA-MB-361 cells were transiently transfected with either NT siRNA or MUCL1 siRNA for 48 h. Cell media was changed and conditioned media was collected 48 h later and assessed by MUCL1 enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). *P<0.01 (n=3). Cell lysates were probed using an anti-MUCL1 antibody. (d) RNA was extracted from cells and assessed for MUCL1 expression by reverse transcription PCR. RNA expression is shown as fold expression in each cell line divided by the median of MUCL1 expression across the panel of cell lines ±s.d. (n=3 technical replicates). For assessing protein levels, cells were grown for 48 h in serum-free media. Culture supernatant was collected and the secreted MUCL1 was measured by ELISA and normalized to the cell number. Intracellular MUCL1 levels were examined in whole-cell lysates by western blotting for comparison. The experiments were repeated twice with similar results.