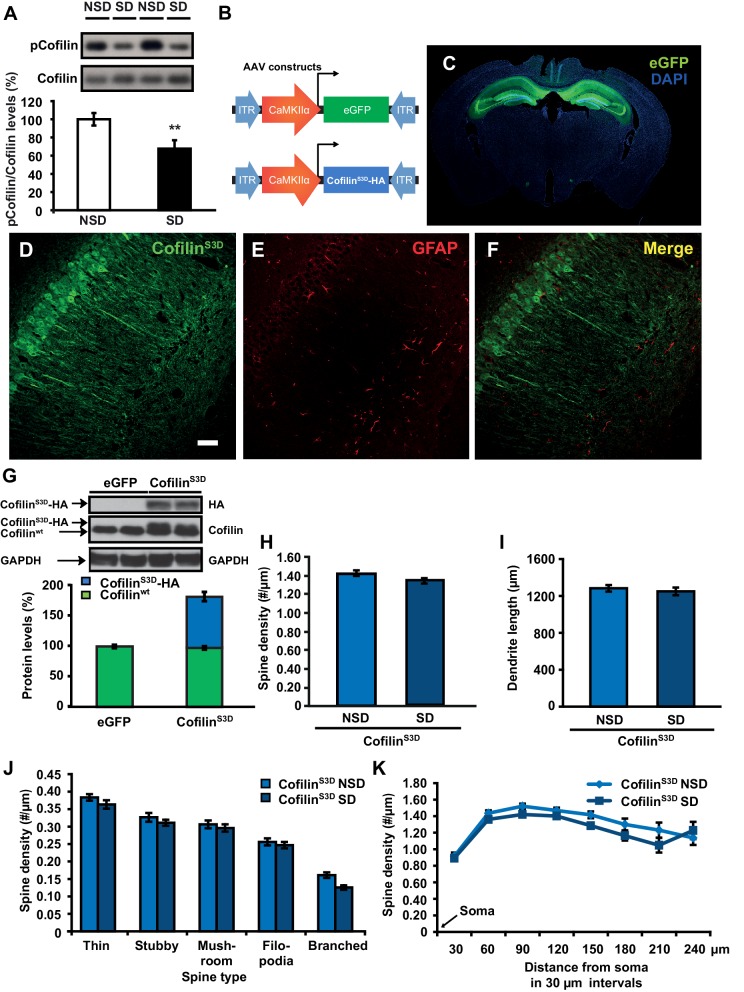
Figure 3. Increased cofilin activity in the hippocampus mediates the spine loss associated with sleep deprivation.
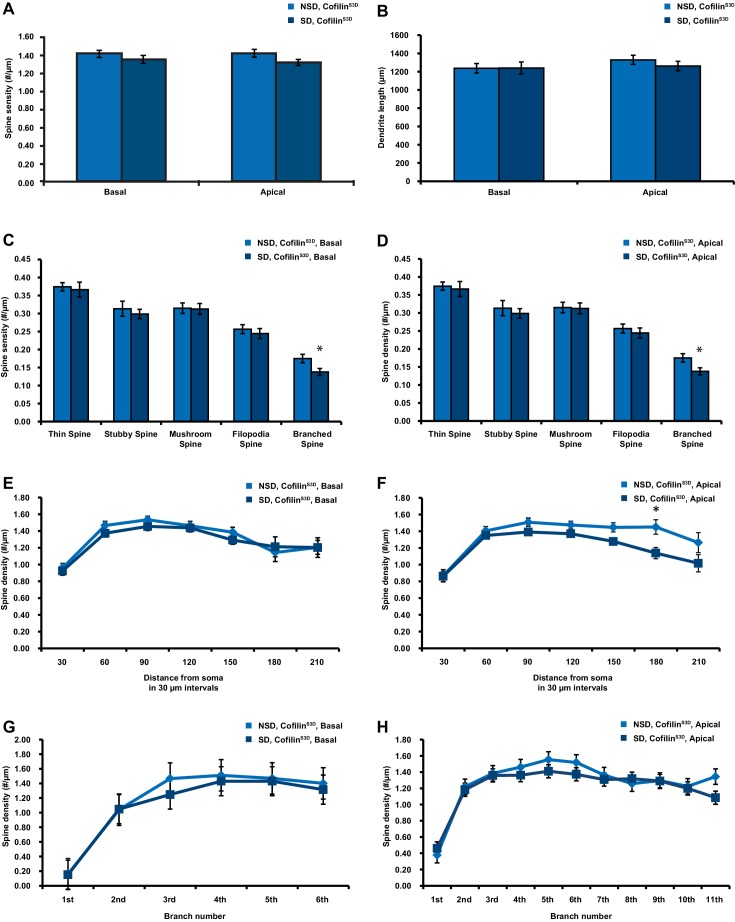
(A) Five hours of sleep deprivation leads to a reduction in cofilin phosphorylation at serine 3 in the hippocampus. A representative blot is shown. Each band represents an individual animal. (n = 13–14, Student’s t-test p=0.0090). (B) Mice were injected with pAAV9-CaMKIIα0.4-eGFP or pAAV9-CaMKIIα0.4-cofilinS3D-HA into the hippocampus to drive expression of eGFP or the mutant inactive form of cofilin (cofilinS3D) in excitatory neurons. This inactive mutant form of cofilin was made by substituting serine 3 for aspartic acid, which mimics a phosphoserine residue. An HA-tag was included to discriminate between mutant and endogenous cofilin. (C) A representative image showing that viral eGFP expression was restricted to the hippocampus. (D–F) CofilinS3D expression was excluded from astrocytes in area CA1 as indicated by a lack of co-labeling (F) between viral cofilin (D) and GFAP expression (E). Scale bar, 100 µM. (G) Virally delivered cofilinS3D protein levels were approximately 75% (blue bar) of wild-type cofilin levels (green bar). Wild-type cofilin levels were not significantly affected by expression of cofilinS3D. An HA-tag antibody was used to detect the mutant inactive form of cofilin. (n = 4). (H) Hippocampal cofilinS3D expression prevents spine loss in apical/basal dendrites of CA1 neurons that is associated with sleep deprivation (n = 6, Student’s t-test, p>0.05). (I) Hippocampal cofilinS3D expression prevents the decrease in apical/basal dendritic spine length in neurons of hippocampal that is caused by sleep deprivation (n = 6, Student’s t-test, p>0.05). (J) Sleep deprivation does not alter the number of any spine type in apical/basal dendrites of CA1 neurons in the hippocampus of mice expressing cofilinS3D (n = 6, Student’s t-test, p>0.05). (K) Sleep deprivation does not attenuate apical/basal spine density at any distance from the soma in mice expressing cofilinS3D (n = 6, Student’s t-test, p>0.05). NSD: non-sleep deprived, SD: sleep deprived. Values represent the mean ± SEM. **p=0.0090. Student’s t test. See also Figure 3—figure supplement 1. For separate analyses of apical and basal spine numbers see Figure 3—figure supplement 2.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.13424.008
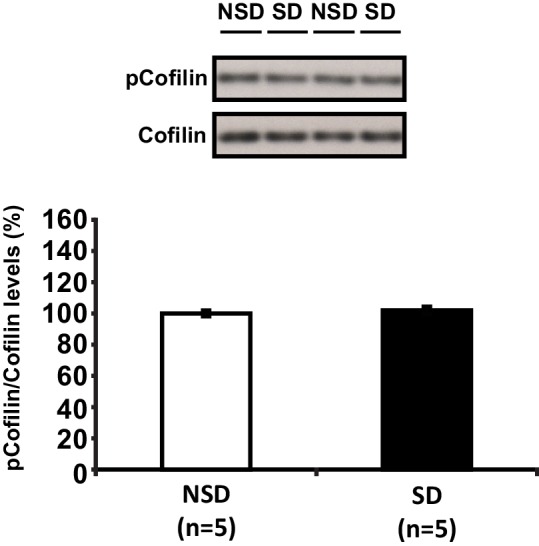
Figure 3—figure supplement 1. Sleep deprivation does not alter cofilin phosphorylation in the prefrontal cortex.