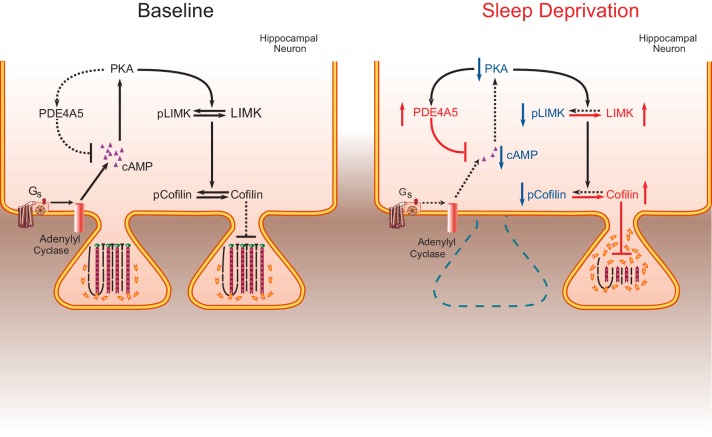
Figure 6. The impact of sleep deprivation on hippocampal spine dynamics.
Sleep deprivation increases PDE4A5 protein levels that cause a reduction in cAMP levels and attenuation of the PKA-LIMK signaling pathway, which results in a reduction in the phosphorylation of cofilin. Dephosphorylated cofilin can lead to spine loss. Suppressing PDE4A5 function through viral expression of a catalytically inactive PDE4A5 prevents alterations in LIMK and cofilin signaling as well as the cognitive impairments caused by sleep deprivation. Likewise, attenuating cofilin activity through viral expression of a catalytically inactive form of cofilin prevents the loss of dendritic spines, impairments in synaptic plasticity, and memory deficits associated with sleep loss. Proteins whose function is reduced after sleep deprivation are shown in blue. Proteins whose function is promoted by sleep deprivation are shown in red.