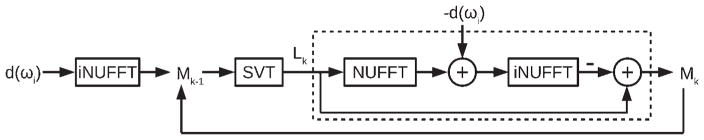
FIG. 1.
LRMC algorithm. The preprocessed k-space data, d(ωi), are converted to image space with an inverse nonuniform fast Fourier transform (iNUFFT). The resulting data Mk–1 are processed with soft singular value thresholding (SVT), which recreates the dataset Lk using only those singular values S > λLSmax, where Smax is the maximum singular value and λL is a constant. Lk is then converted back to k-space and the original k-space data are subtracted from it. The difference, representing residual aliasing artifacts, is converted to image space and subtracted from Lk to form the reconstructed data Mk. This process is iterated until |Mk – Mk−1| < tol, where tol is the desired tolerance for convergence.