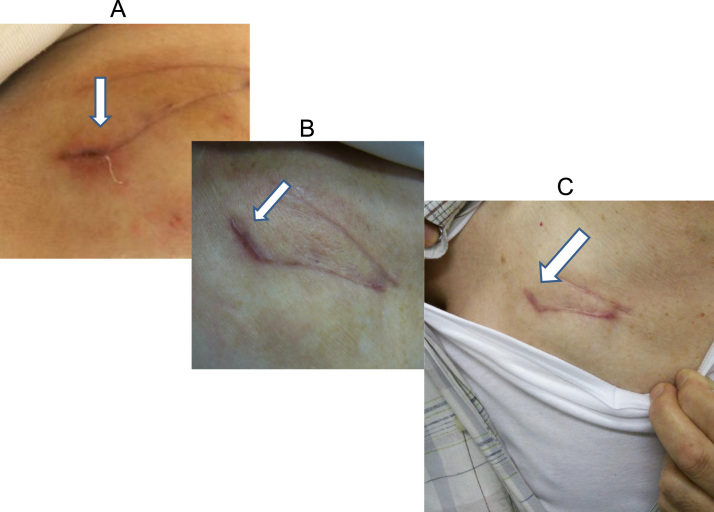
Fig. 2.
A case of superficial incisional infection. Fourteen days after an operation to exchange a pacemaker device, wound dehiscence was observed at the sutured incision line (panel A). Inflammatory markers became elevated, and intravenous antibiotics were administered for 11 days in conjunction with daily wound irrigation. About one month later, the incisional wound was closed, with complete resolution of inflammatory markers (panel B). There was no fever or inflammatory marker elevation during a follow-up period of 6 months. The incisional wound remained clear (panel C).