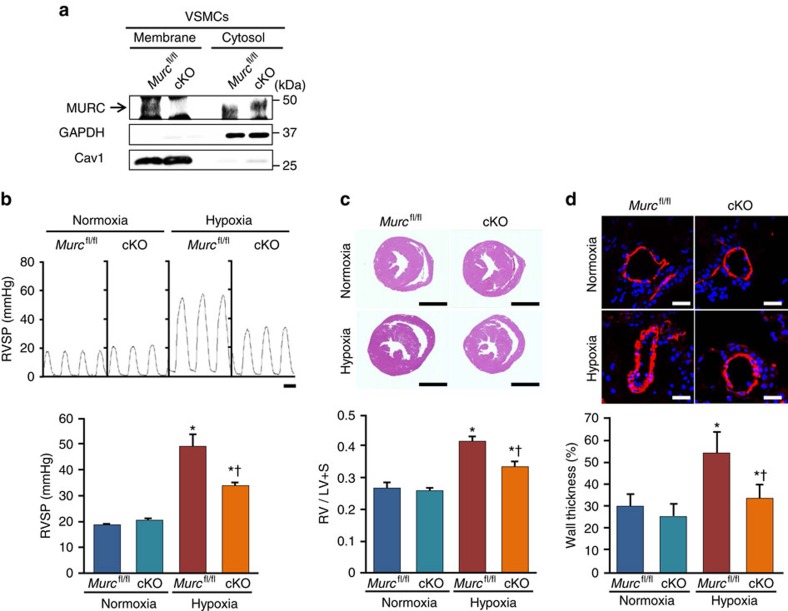
Figure 4. Attenuation of PH induced by hypoxia in Murc conditional knockout mice.
(a) VSMCs were isolated from Murcfl/fl and cKO aortae. Lysates of Murcfl/fl and cKO VSMCs were immunoblotted with an anti-MURC antibody. Membrane and cytosol fractions were separated by the gradient of sucrose. (b) Murcfl/fl and cKO mice were exposed to normobaric hypoxia (10% O2) for 4 weeks, and RV hemodynamics was then measured (n=5–7 per group). Scale bar, 100 ms. (c) Relative RV weights of Murcfl/fl and cKO mice were determined as the ratio of the RV weight to the LV and septum weights (RV/LV+S) (n=6–7 per group). Scale bar, 2 mm. (d) Pulmonary vascular remodelling was assessed by measuring the medial thickness of alveolar/distal pulmonary vessels of 25–100 μm in diameter from lung sections immunostained with αSMA from 5–6 images from different fields (n=4–5 per group). Per cent wall thickness is expressed as the medial wall area divided by the area of the vessel. Scale bar, 20 μm. *P<0.05 compared with the respective normoxic group, †P<0.05 compared with the hypoxic WT group. Data are presented as mean±s.e.m. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6.