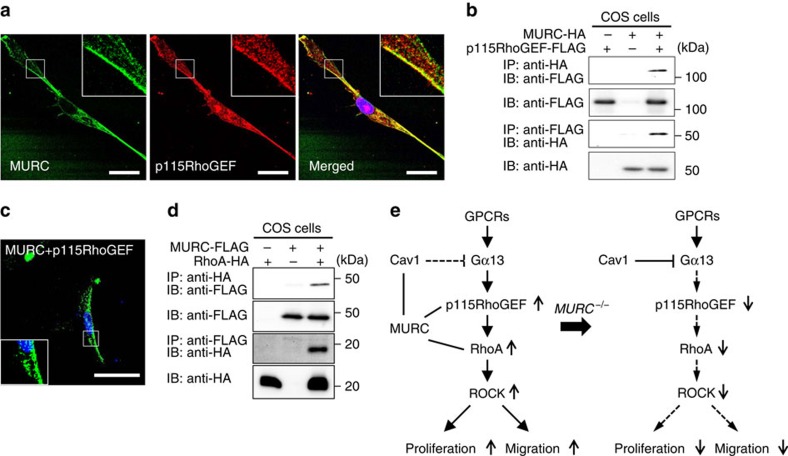
Figure 7. Association of MURC with RhoA and p115RhoGEF.
(a) Immunostaining images of MURC and p115RhoGEF in hPASMCs. Scale bar, 20 μm. (b) pcDNA3.1-hMURC-HA and/or pCS2FLAG-hp115RhoGEF were cotransfected into COS cells, and the cell lysates were then immunoprecipitated with anti-HA and anti-FLAG antibodies. (c) hPASMCs were transfected with phmKGN-MC-hMURC and phmKGC-MN-hp115RhoGEF. Scale bar, 50 μm. (d) COS cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-hMURC-FLAG and/or pcDNA3.1-hRhoA-HA and cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-FLAG and anti-HA antibodies. (e) Proposed roles of the MURC-mediated activation of Rho/ROCK signalling in PASMCs. When MURC is present, it associates with Cav1, leading to reductions in the association between Cav1 and Gα13, which facilitates the interaction of Gα13 with p115RhoGEF, thereby activating the Rho/ROCK pathway. MURC also serves as a platform to compartmentalize p115RhoGEF and RhoA at caveolae. In the absence of MURC, Cav1 interacts with Gα13 and inhibits the association of Gα13 with p115RhoGEF, leading to the suppression of the Rho/ROCK pathway. Uncropped images of blots are shown in Supplementary Fig. 6.