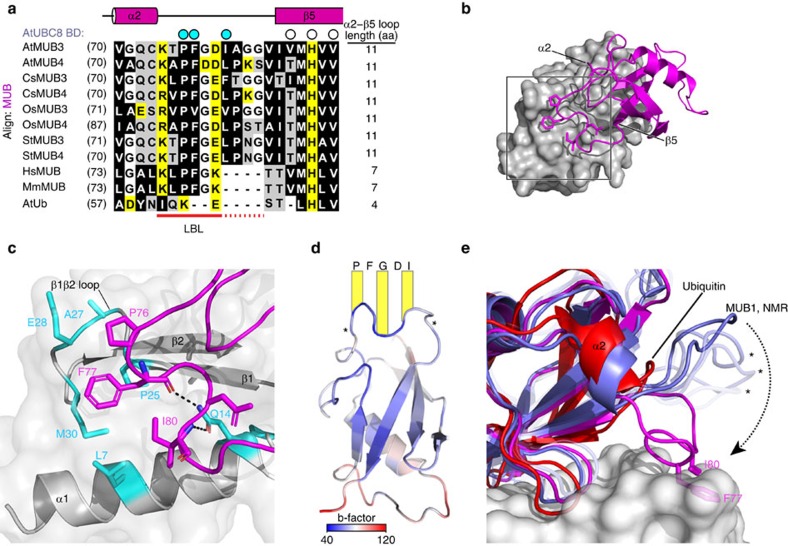
Figure 4. The MUB LBL is stabilized by E2 surface interaction.
(a) Structure-based sequence alignment for the LBL region of the AtMUB3/4 protein family from Arabidopsis, Arabidopsis thaliana (At); cucumber, Cucumis sativus; rice, Oryza Sativa (Os); potato, Solanum tuberosum (St) and the single MUB proteins from human, Homo sapiens (Hs) and mouse, Mus musculus (Mm). Ubiquitin is included for comparison. Residues in direct contact with E2 (AtUBC8 BD) are indicated by circles above the alignment, among which, cyan circles indicate LBL residues and open circles indicate BBS-binding residues. The most universally conserved part of the LBL is underlined in red, while plant-specific conservation is underlined with red dots. The aligned amino acids are coloured black (hydrophobic), yellow (charged) and white (polar) and the length of the α2β5-loop is indicated to the right. (b) Structure of the AtMUB3 LBL is highlighted by a square, with AtUBC8 in surface structure (grey) and AtMUB3 in cartoon structure (magenta). Secondary structures flanking the LBL in AtMUB3 are indicated. (c) Detailed view of the AtMUB3 LBL and AtUBC8 with interacting residues rendered with sticks. LBL (magenta) and AtUBC8 (grey) with residues coloured in cyan. Salt bridges are shown as dashed lines. (d) b-factors are plotted on AtMUB3 (cartoon) viewed from the E2 perspective. Core residues of the bar are listed and flexible side arms are indicated with asterisks. (e) Superposition of Ub (red) modelled from a backside Ube2D3-binding structure, AtMUB1 alone in solution (purple blue) and the AtMUB3 (magenta):AtUBC8 (grey, surface) complex. LBLs in different states of the AtMUB1 NMR structure (asterisks) exhibit flexibility and various ‘open' conformations, while LBL residues in the AtMUB3 structure (sticks) are coordinated by the E2 surface demonstrating a ‘closed' conformation.