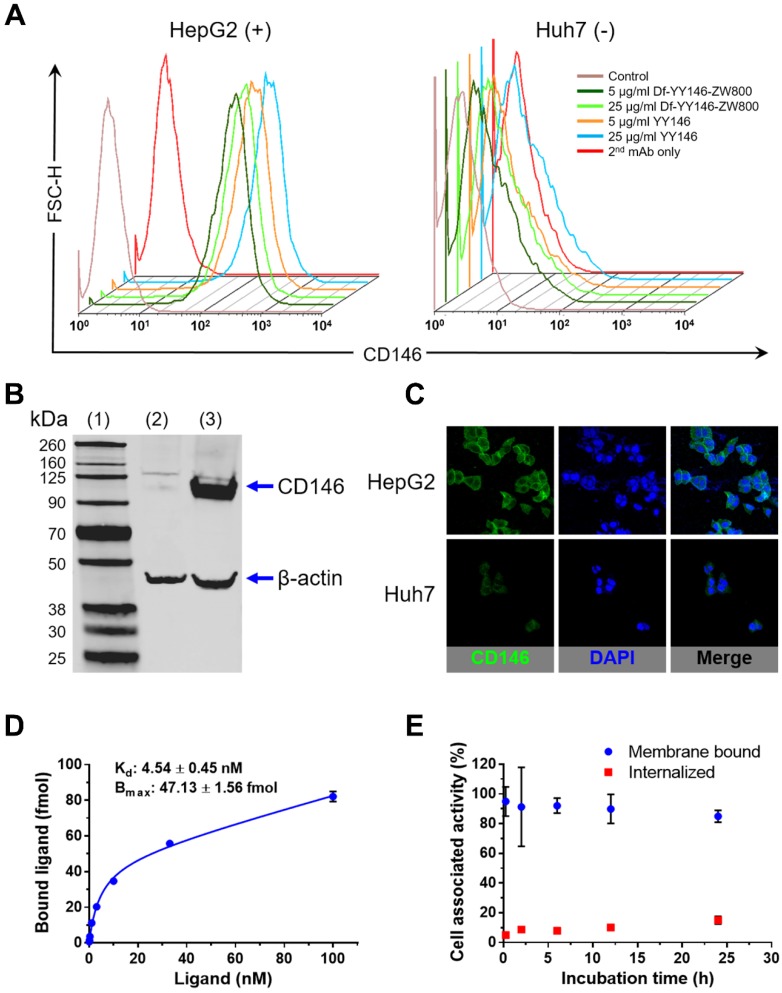
Figure 1.
In vitro CD146 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells. A) Flow cytometry of HepG2 and Huh7 HCC cells. Fluorescence histograms revealed markedly higher signal, indicative of higher CD146 expression, for HepG2 cells compared to Huh7 cells. B) Western blot displayed a strong band around 110 kDa consistent with CD146 (113 kDa) in HepG2 cell lysates; such band was undetectable in Huh7 cells. (1) molecular weight ladder; (2) Huh7 lysate; (3) HepG2 lysate. C) Consistent with results from A and B, immunofluorescence staining showed very intense CD146 staining (green channel) of HepG2 cell membranes that was unmatched in Huh7 cells. D) CD146 saturation binding assay isotherm in HepG2 cells. Cells were incubated with increasing concentration of radiolabeled YY146 (0.03-100 nM). The affinity constant (Kd) and maximum ligand binding (Bmax) were determined from the analysis of the binding isotherm. E) Cell internalization assay showing the slow kinetics of 89Zr-Df-YY146 internalization.