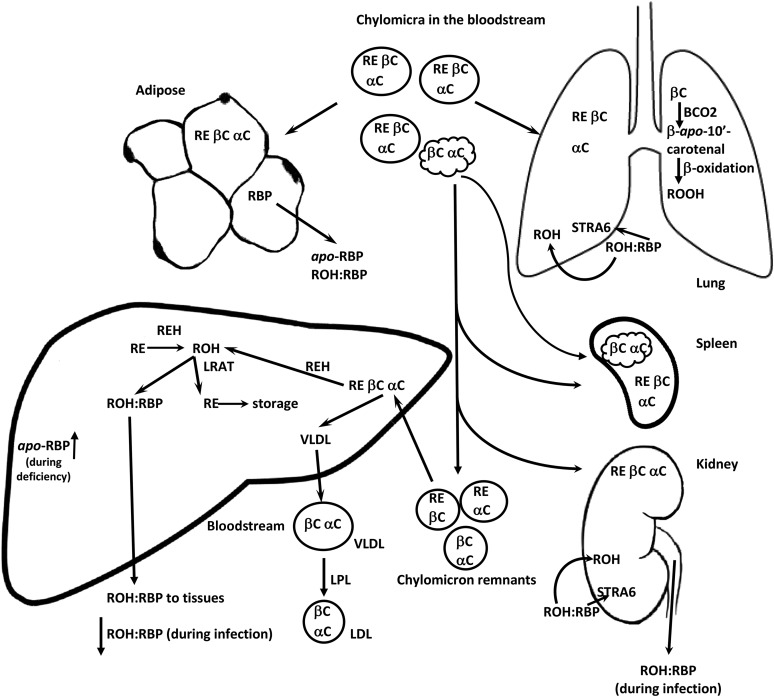
FIGURE 4.
After absorption, retinyl esters and carotenoids can be released from chylomicra into tissues. Malformed chylomicra can be scavenged by the spleen. However, the bulk of retinyl esters and carotenoids make their way to the liver in chylomicron remnants. In the liver, the retinyl esters can be hydrolyzed by retinyl ester hydrolase. Retinol can then be either complexed with RBP and released into the plasma or re-esterifed by LRAT for long-term storage. The carotenoids can be cleaved to retinol (although not a major pathway in the liver), stored, or packaged into VLDLs and released into the circulation. Retinol uptake from RBP by cells can be facilitated by STRA6. BCO2, β-carotene 9,10-oxygenase; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; LRAT, lecithin:retinol acyltransferase; RBP, retinol-binding protein; RE, retinyl esters; REH, retinyl ester hydrolase; ROH, retinol; ROOH, retinoic acid; STRA6, stimulated by retinoic acid 6 receptor; αC, α-carotene; βC, β-carotene.