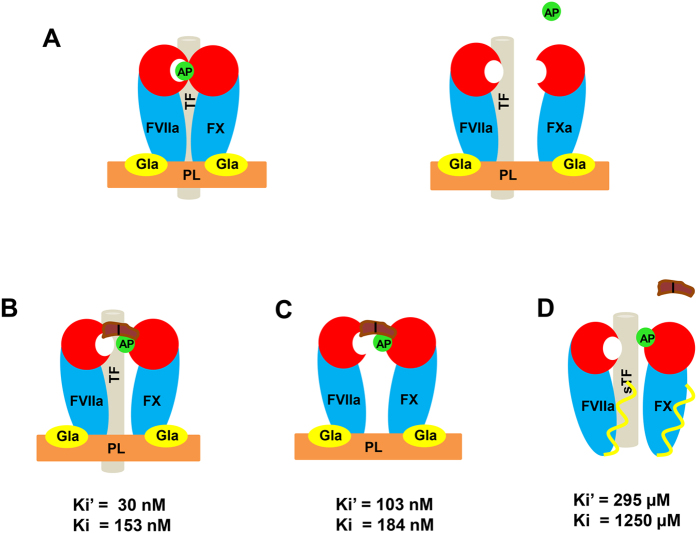
Figure 7. Proposed inhibitory mechanism of exactin.
(A) Proteolytic activation of the macromolecular substrate FX by ETC via the cleavage of activation peptide (represented as AP) at Arg152-Ile153 bond. (B) Exactin (represented as I) exhibits a mixed-type inhibition to complete extrinsic complex by binding to a site away from the active site of FVIIa there by significantly reducing FX proteolysis. (C) The removal of TF from the extrinsic complex however, does not alter the binding affinity of exactin and the inhibitor is able to inhibit FX proteolysis significantly. (D) The removal of phospholipids (PL) from the ETC drastically reduced (>1000-folds) the inhibition of FX proteolysis by exactin. In the absence of phospholipids, the position and conformation of Gla domain may be different and thus leading to loss of affinity.