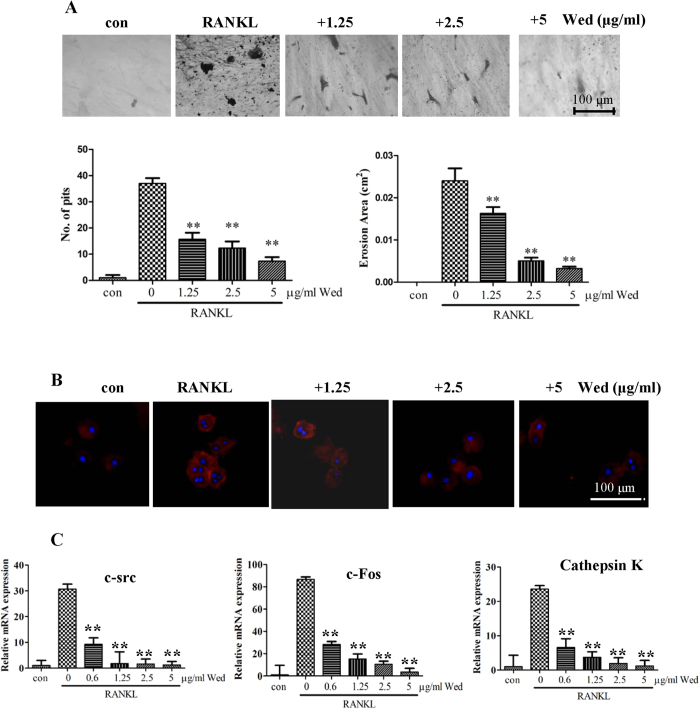
Figure 3. Wedelolactone inhibits bone resorption in RAW264.7 cells.
(A) Wedelolactone suppressed formation of bone resorption pits. RAW264.7 cells (1 × 105 cells) were treated with 100 ng/ml RANKL for 4 d and then incubated with or without wedelolactone on dentine slices for 2 d. Dentine slices were stained with Mayer’s hematoxylin after removal of cells. The resorption pits were visualized with light microscopy. The numbers of pits and erosion areas were analyzed with Image-Pro Plus software (bottom). (n = 3). Error bars denote mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. RANKL-treated control. (B) Wedelolactone suppressed RANKL-induced actin ring formation in RAW264.7 cells. RAW264.7 cells (1 × 105 cells) were incubated with RANKL for 4 d and then treated with wedelolactone for 2 d. Cells were fixed and stained for F-actin. (C) Wedelolactone inhibited mRNA levels of c-src, c-fos and cathepsin k. Wedelolactone was pretreated with or without wedelolactone for 6 d in the presence of RANKL. Cell lysates or total RNA was subjected to qRT-PCR. (n = 3). Error bars denote mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 vs. RANKL-treated control.