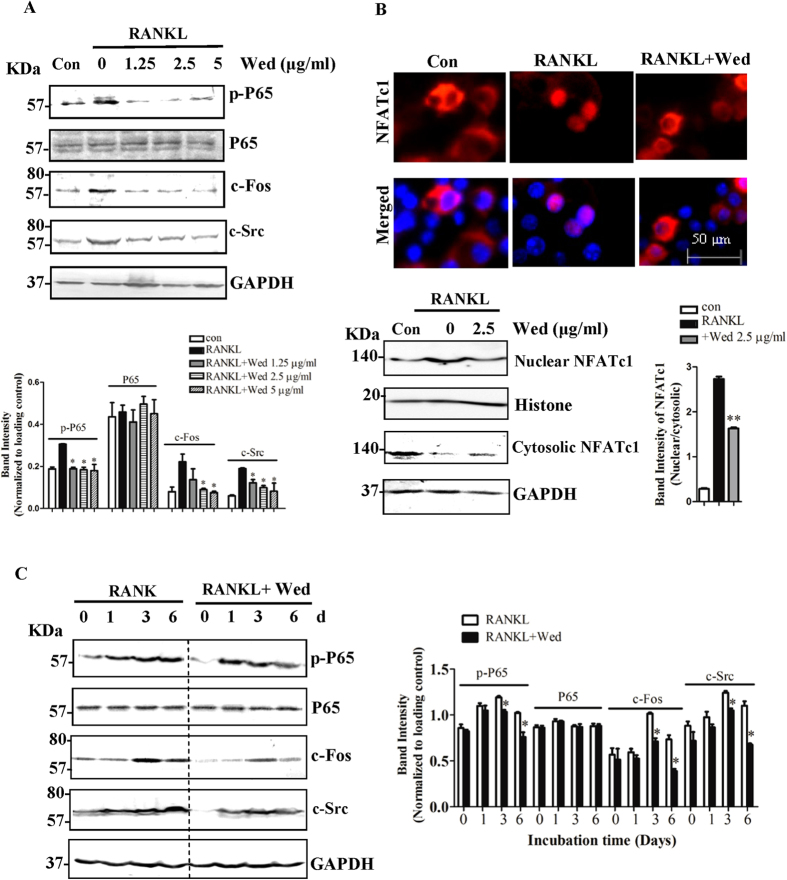
Figure 4. Wedelolactone inhibits RANKL-induced NF-κB/NFATc1 pathway.
(A) Wedelolactone inhibited phosphorylation of p65, and suppressed c-Fos as well as c-src expression stimulated by RANKL. RAW264.7 cells were incubated with or without wedelolactone and then stimulated with 30 ng/ml RANKL for 6 d. The cell lysates were extracted and subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (n = 3). (B) Wedelolactone inhibited RANKL-induced NFATc1 nuclear translocation. RAW264.7 cells were incubated with or without wedelolactone and then stimulated with 30 ng/ml RANKL for 6 d. The location of NFATc1 was visualized by immunofluorescence analysis (Magnification ×400) and quantified by Western blot analysis.(n = 3) (C) Wedelolactone inhibited phosphorylation of p65, and suppressed c-Fos as well as c-src expression after 1, 3, 6 d incubation with RANKL. RAW264.7 cells were incubated with or without wedelolactone and then stimulated with 30 ng/ml RANKL for indicated time. The cell lysates were extracted and subjected to Western blot analysis with the indicated antibodies. (n = 3). Error bars (A–C) denote mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.