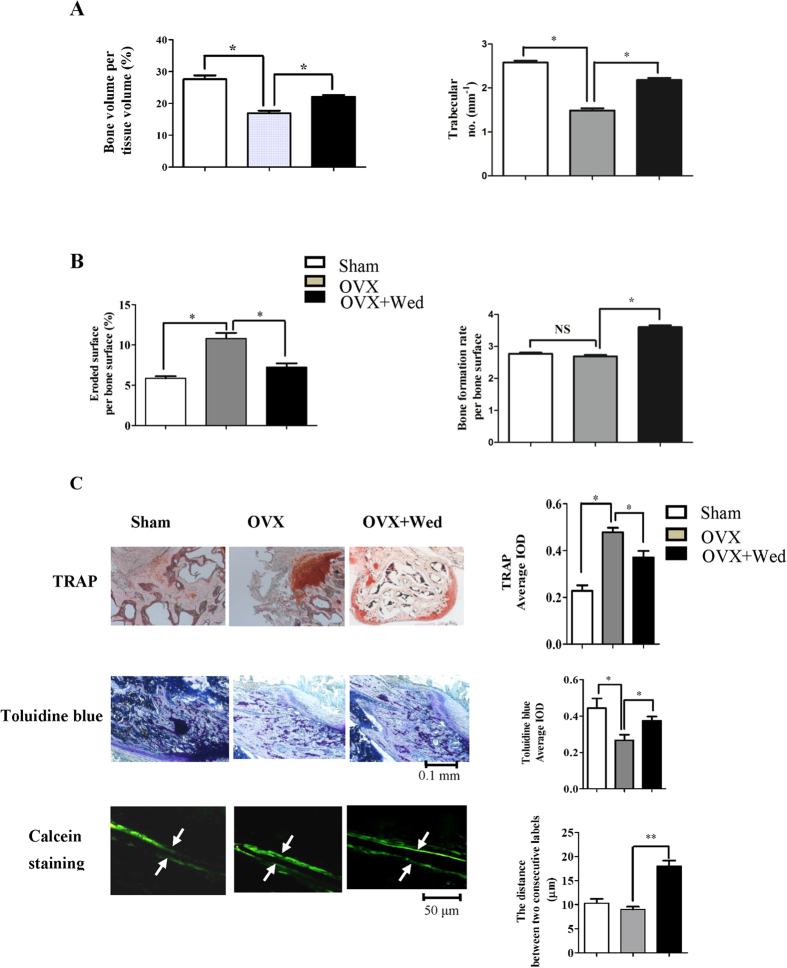
Figure 5. Wedelolactone prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity and enhancing osteoblast activity.
(A) Bone histomorphometric analysis of trabecular bones from 2 month-old female mice. Bone volume/tissue volume and trabecular number was analyzed with osteoMeasure Analysis System. (n = 5–6). (B) Eroded surface/bone surface for osteoclastic bone resoption and bone formation rate per bone surface were analyzed. (n = 5–6). NS: no significance. (C) Histological analysis of the femur of sham-operated (Sham), ovariectomized (OVX) and wedelolactone-treated OVX mice (n = 4–6). Up: TRAP staining of the proximal tibiae of Sham, OVX and wedelolactone-treated OVX mice. Middle: Toluidine blue staining of the proximal tibiae of Sham, OVX and wedelolactone-treated OVX mice. Bottom: New bone formation was determined by calcein double labeling. Arrows mark distance between calcein-labelled layers. TRAP staining and Toluidine blue staining were quantified by average IOD, and the distance between two consecutive labels in the proximal tibiae was quantified with Image-Pro Analyzer 6.2 software (Media Cybernetics, Bethesda, MD, USA). Error bars (A–C) denote mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.