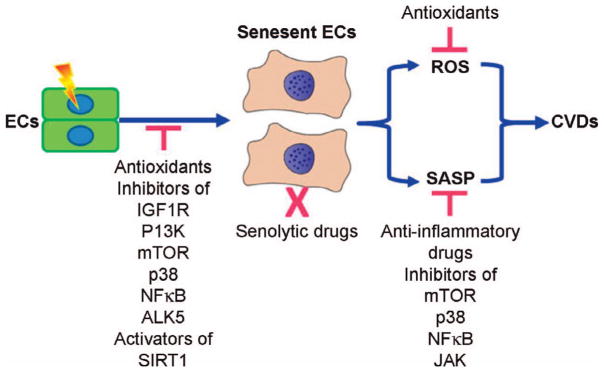
FIG. 3.
Potential strategies to prevent, mitigate, and treat radiation-induced CVDs by targeting senescent endothelial cells. Antioxidants, inhibitors of insulin/insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF1R), phosphtidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K), mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), p38, NFκB and TGF-β type 1 receptor (ALK5), and the activators of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) may be used to prevent radiation-induced CVDs by inhibiting the induction of endothelial cell (EC) senescence. Clearance of senescent cells with a senolytic drug that can selectively kill senescent cells including senescent endothelial cells has the potential to be developed as novel therapeutic strategy to mitigate and treat radiation-induced CVDs. Antioxidants and inhibitors of mTOR, p38, NFκB, and Janus kinase (JAK) may prevent, mitigate, and treat radiation-induced CVDs by scavenging senescent cell-produced reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibiting senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), respectively.