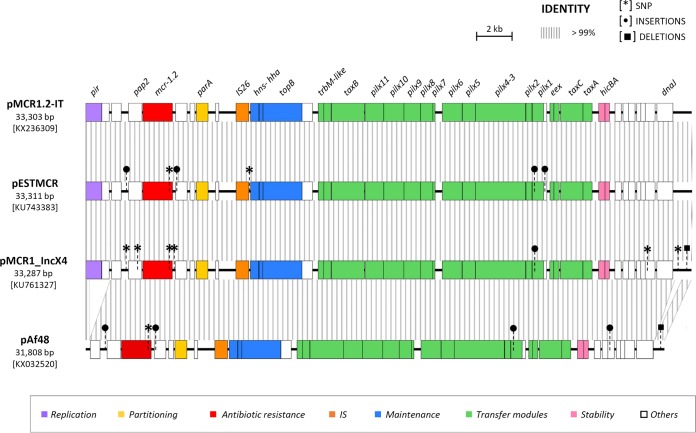
FIG 1.
Linear map of plasmid pMCR1.2-IT and comparison with previously sequenced mcr-1-carrying IncX4 plasmids. Homologous segments are indicated by striped shading, representing ≥99% sequence identity. Genes encoding proteins of known functions are in different colors, as detailed in the legend. Differences at the sequence level, including single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), insertions (IS), and deletions, are shown by different symbols. Compared to pMCR1.2-IT, pESTMCR, pMCR1-incX4, and pAf48 differed in 2, 6, and 1 SNPs, respectively. In pESTMCR, SNPs were located within the mcr-1 gene and in an intergenic region adjacent to hns (n = 1). In pMCR1-IncX4, SNPs were located within the mcr-1 gene, within pap2 (n = 1), in intergenic regions (n = 2), in a gene coding for a hypothetical protein (n = 1), and in the iteron region (n = 1); in genes coding for the PAP2 transmembrane protein and for MCR, nucleotide substitutions led to missense mutations. In pAf48, the single SNP was located within the mcr gene; deletions of 1,160 bp and of 388 bp were present in the replication region, affecting the pir gene and a region upstream of dnaJ, respectively. Other differences consisted of the following: (i) a 22-bp deletion located in the iteron region in pMCR1-incX4; (ii) an insertion of a single nucleotide downstream of the gene coding for the PAP2 protein and of 5 nucleotides within a gene encoding a hypothetical protein upstream of mcr-1 in pESTMCR and pAf48; (iii) a 48-bp insertion within a gene encoding a hypothetical protein located between hicA and dnaJ and a 2-bp deletion within the iteron region in pAf48; and (iv) a single nucleotide insertion within the pilX1 gene in pMCR1-incX4, pESTMCR, and pAf48.