FIG 2.
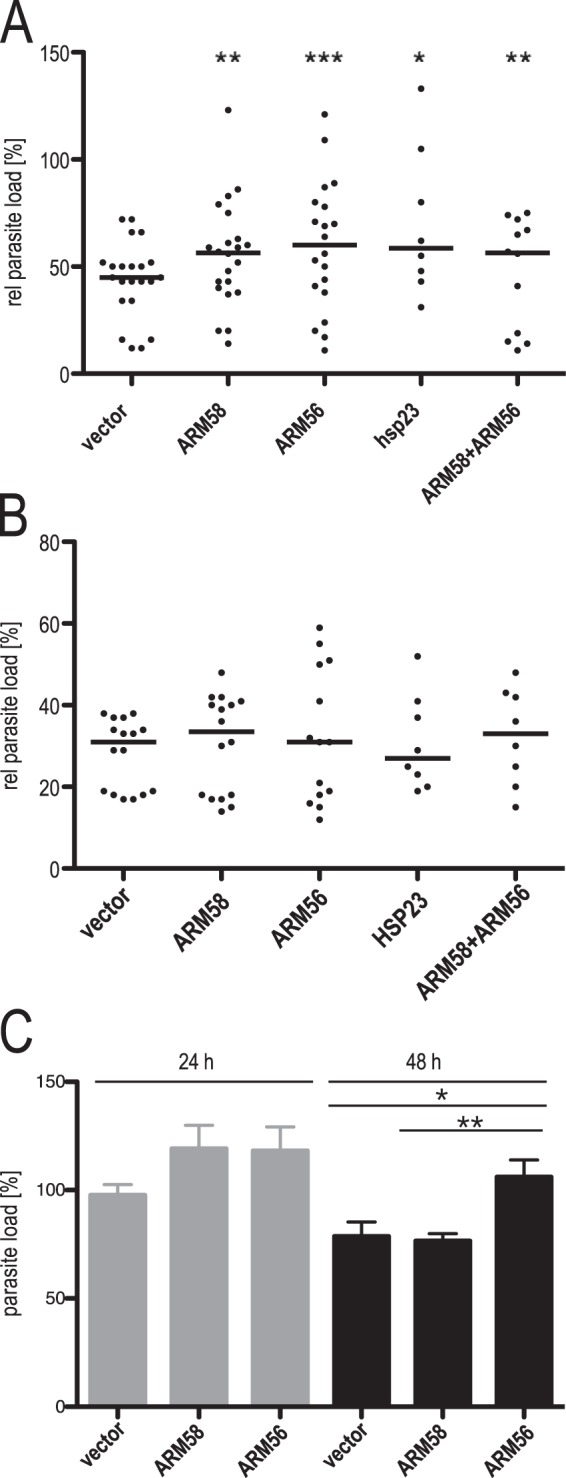
(A) In vitro infection of bone marrow-derived macrophages and treatment with sodium stibogluconate. L. donovani parasites transfected with the vector, ARM58, ARM56, HSP23, or the ARM58-ARM56 transgene were used to infect BMMs at an MOI of 5:1. After 24 h, 160 μg ml−1 sodium stibogluconate was added and incubation was continued for 48 h. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001 (n = 6 to 24). Parasite load quantification was done by qPCR as described in Materials and Methods; the relative (rel) parasite load was defined as the parasite load after treatment as a percentage of the parasite load in untreated cells. (B) In vitro infection of bone marrow-derived macrophages and treatment with miltefosine. L. donovani parasites transfected with the vector, ARM58, ARM56, HSP23, or the ARM58-ARM56 transgene were used to infect BMMs at a multiplicity of infection of 5:1. At 24 h after infection, miltefosine was added to the cultures at 30 μM, and incubation was continued for 48 h. Parasite load quantification was done by qPCR as described in Materials and Methods; the relative parasite load was defined as the parasite load after treatment as a percentage of the parasite load in untreated cells (n ≥ 6). (C) Parasite load quantification after in vitro infection of BMMs with L. donovani with pCLN and the ARM58 and ARM56 transgenes. Parasite load quantification was done by qPCR as described in Materials and Methods, with the value for control parasites at 24 h being set equal to 100%. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 (n = 8).
