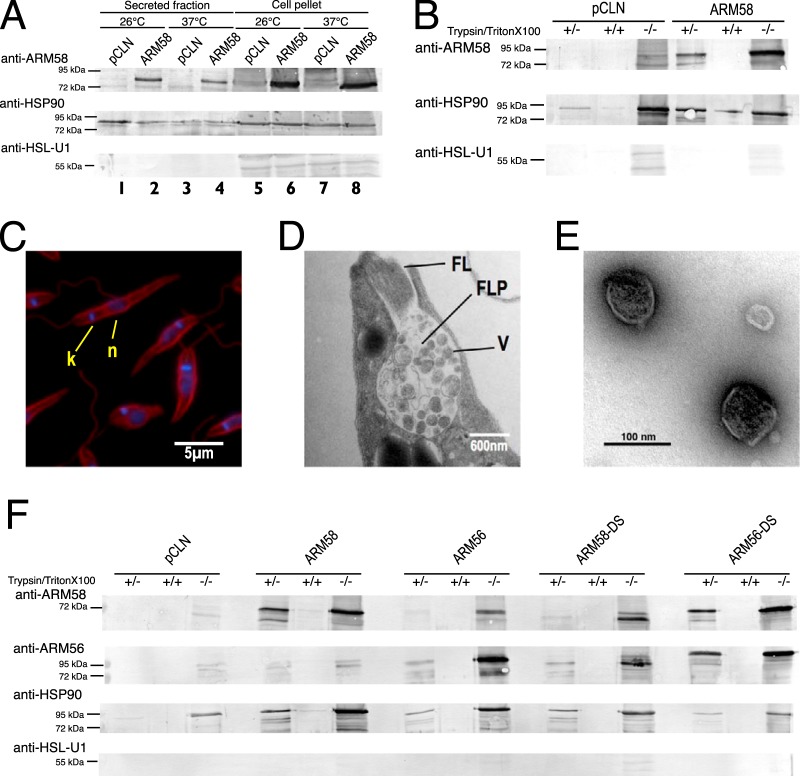
FIG 4.
(A) Detection of ARM58 in L. donovani promastigotes and in the secreted protein fraction. L. donovani parasites transfected with pCLN or ARM58 transgenes were incubated for 2 h at 25° or 37°C in serum-free medium. After centrifugation, medium supernatants and sedimented cells were concentrated by acetone precipitation and dissolved in SDS sample buffer, followed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Immunological staining was performed with anti-ARM58, anti-HSP90 (secreted fraction marker), and anti-HSL-U1 (nonsecreted) antibodies. (B) Testing of secretome proteins for sensitivity to trypsin in the presence and absence of Triton X-100 detergent. Antibody detection was as described in the legend to panel A. (C) Antitubulin and DAPI staining of the promastigotes after harvesting of exosomes from cell supernatant. Cells were fixed and stained, followed by fluorescence microscopy. k, kinetoplast; n, nucleus. (D) Ultrastructure of the flagellar pocket of L. donovani promastigotes at 37°C, showing vesicles (V) in the flagellar pocket (FLP) and the flagellum (FL). (E) Isolated exosomes visualized by negative staining and transmission electron microscopy. (F) Detection of ARM58 and ARM56 in exosomes. L. donovani with pCLN, ARM58, ARM56, ARM58-DS, and ARM56-DS transgenes were incubated for 2 h in serum-free medium at 37°C. Culture supernatants were collected and subjected to exosome enrichment. Exosome fractions were then treated with trypsin alone or a combination of trypsin and Triton X-100. Before and after trypsin digestion, samples were precipitated with acetone, redissolved in SDS sample buffer, and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. Proteins were detected with anti-ARM58, anti-ARM56, anti-HSP90 (exosomal marker), and anti-HSL-U1 (nonexosomal protein) antibodies. −/−, nondigested exosome preparations; +/+, exosome preparations subjected to trypsin proteolysis in the presence of Triton X-100 detergent; +/−, exosome preparations subjected to trypsin proteolysis in the absence of Triton X-100 detergent.