Fig. (4).
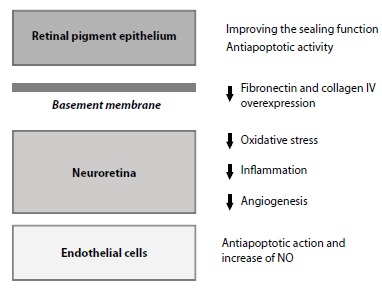
Effects of fenofibrate in diabetic retinopathy. This figure summarizes the reported effects of FA (the active metabolite of fenofibrate) on several retinal components such as RPE, BM, neuroretina and endothelial cells. In RPE (outer blood retinal barrier), FA prevents the disorganisation of tight junctions proteins and the hyperpermeability. In addition, FA elicits a dual protective effects by down-regulation of stress-mediated signalling and induction of autophagy and survival pathways. In BM, FA downregulates the overexpression of fibronectin and collagen IV, thus further reducing the increase in permeability. In the neuroretina FA exerts antioxidant, antinflammatory and antiangiogenic actions. Finally, in the endothelial cells, FA induces an antiapoptotic action and stimulates NO synthase phosphorylation and NO production. Abbreviations: BM, basement membrane; FA, Fenofibric acid; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; NO, nitric oxide.
