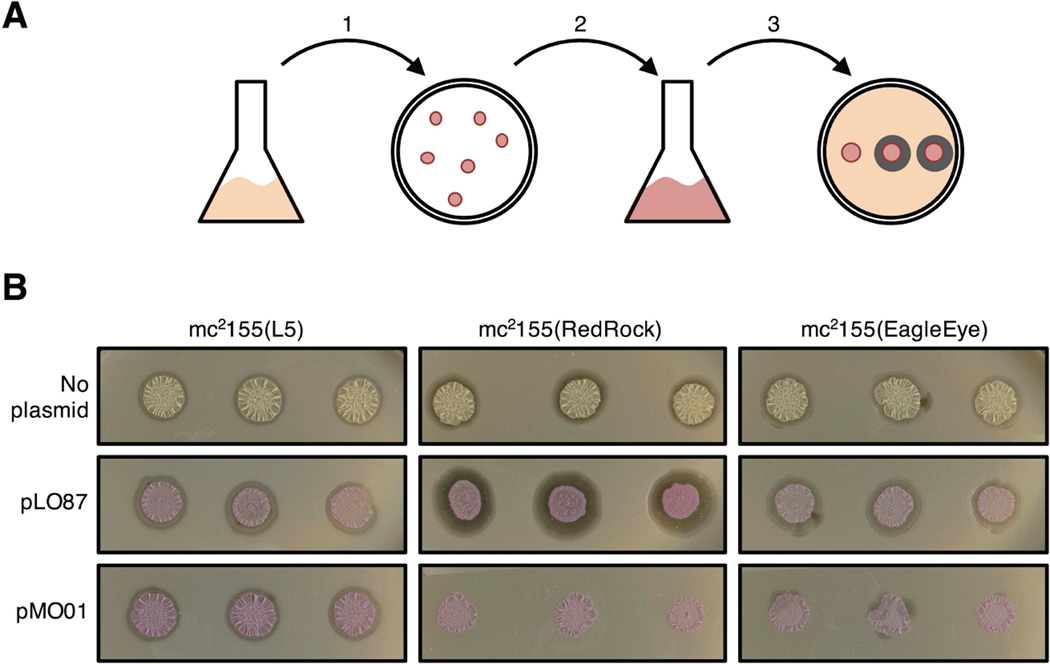
Figure 7.
Phage RedRock par-mediated incompatibility. A. Scheme to test for parABS-mediated incompatibility. Plasmids pMO01 (carrying RedRock parABS and mCherry), pLO87 (lacking parABS) were electroporated into M. smegmatis lysogens of L5, RedRock, or EagleEye. and kanamycin-resistant transformants selected (step 1). Three individual red transformants (or un-transformed control colonies) were propagated in liquid selective media (step 2), and spotted onto a lawn of wild type M. smegmatis to test for phage release (seen as rings of infection surrounding spotted cultures) indicating lysogeny (step 3). B. Plasmid MO01 displaces the RedRock prophage. Three independent transformants carrying pMO01 show no spontaneous phage release indicating prophage loss, which is dependent on parABS (pLO87 transformants of RedRock lysogen all show phage release). All transformants and (untransformed cells) of an L5 lysogen show prophage maintenance and compatibility. Spontaneous phage release is reduced in pMO01 transformants of the EagleEye lysogen suggesting partial incompatibility between the RedRock parABS in pMO01 and the EagleEye prophage.