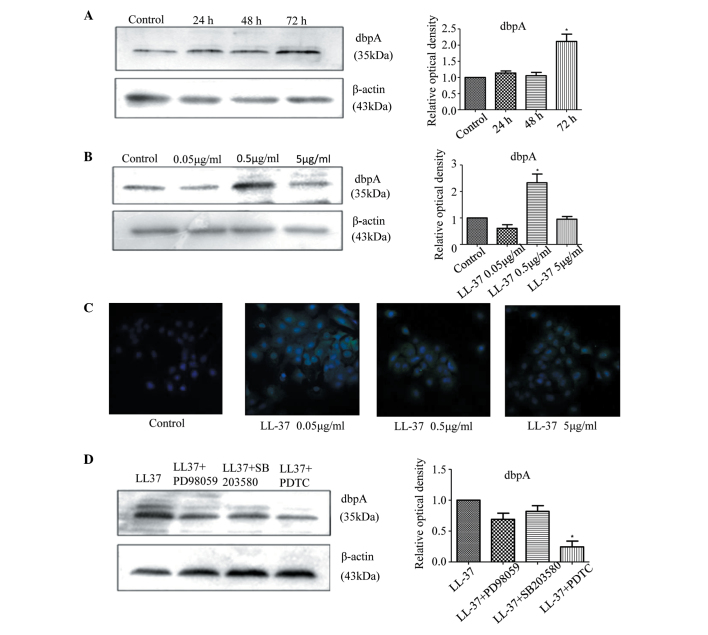
Figure 4.
(A and B) LL-37 promotes the upregulation of dbpA protein in A431 cells. Time effect: A431 cells were stimulated with 0.5 µg/ml LL-37 for the specified durations. Dose effect: A431 cells were stimulated with the specified doses of LL-37 for 48 h. DbpA protein levels were determined by western blotting. The figure shows the ratio of dbpA protein/β-actin protein. The results from three independent experiments are shown as the mean ± standard deviation. (C) LL-37 promotes the upregulation of dbpA protein in A431 cells. The A431 cells were stimulated with the specified dose of LL-37 for 48 h, and dbpA protein expression levels were determined by immunofluorescence. The figures show dbpA protein fluorescence intensity after stimulation by different concentrations of LL-37. Magnification, ×400. (D) The NF-κB signalling pathway is involved in the upregulation of dbpA stimulated by LL-37 in A431 cells. The A431 cells were pretreated for 30 min with MAPK kinase-extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibitor (PD98059; 10 µM), MAPK inhibitors (SB203580, 10 µM) or NF-κB inhibitor (PDTC; 1 µM), followed by treatment with 0.5 µg/ml LL-37 for 48 h. The protein levels of dbpA were determined by western blotting. The figure shows the ratio of dbpA protein/β-actin protein. The results from three independent experiments are shown as the mean ± standard deviation. *P<0.05 vs. control. MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase; dbpA, DNA-binding protein A; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB.