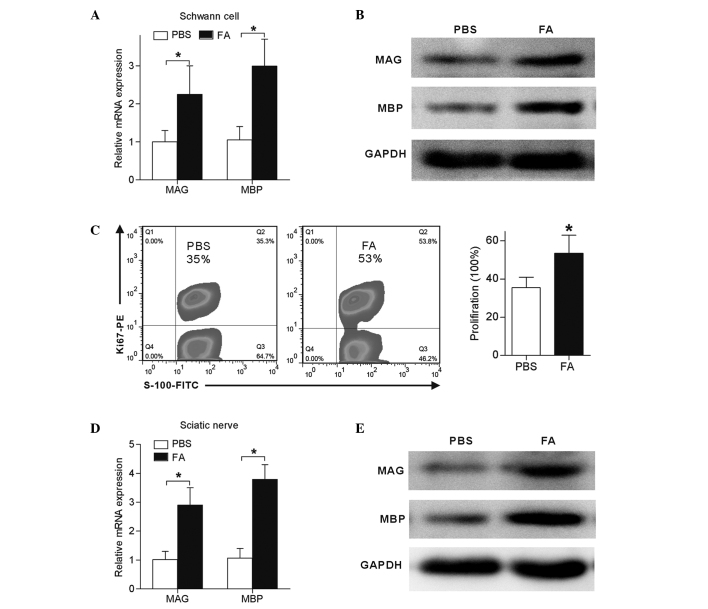
Figure 7.
FA treatment promoted rat sciatic nerve myelination following crush injury. Treatment with FA (50 mg/kg/day for 7 days; n=6) or PBS of the same volume (n=6) was intraperitoneally injected to rats subsequent to crush injury. At 4 weeks after injury, the rats were sacrificed to extract the sciatic nerves and isolate Schwann cells for analysis. (A) mRNA and (B) protein expression levels of MAG and MBP in Schwann cells were significantly upregulated following FA treatment. (C) Ki-67-positive Schwann cells in sciatic nerves, as observed by flow cytometry. (D) mRNA and (E) protein expression levels of MAG and MBP in the sciatic nerve were significantly upregulated following FA treatment. Data in the graphs are shown as the mean ± standard error of three separate experiments. *P<0.05. MAG, myelin-associated glycoprotein; MBP, myelin basic protein; FA, ferulic acid.