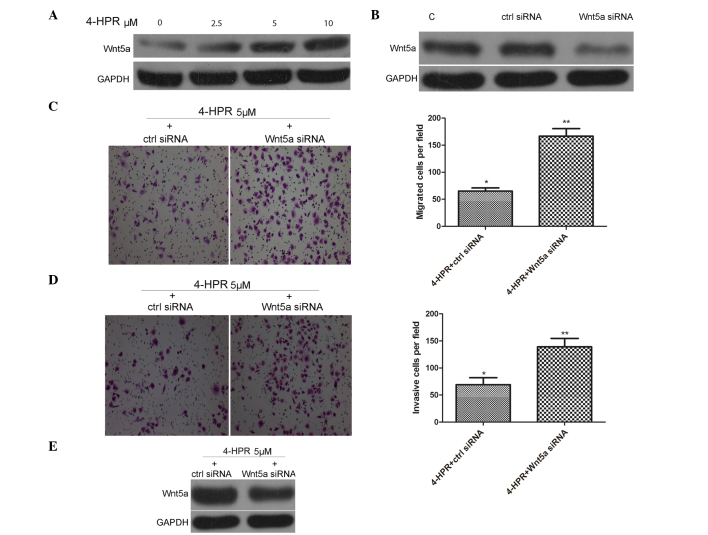
Figure 2.
4-HPR inhibits the migration and invasion of EJ cells by increasing the expression of Wnt5a. (A) EJ cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of 4-HPR for 48 h, and the protein levels of Wnt5a were measured by western blotting. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (B) EJ cells were transfected with ctrl siRNA and Wnt5a siRNA, and the protein levels of Wnt5a were measured by western blotting. GAPDH was used as an internal control. (C and D) EJ cells were transfected with ctrl siRNA and Wnt5a siRNA for 24 h. After incubation with 4-HPR for 48 h, the cells were analyzed by (C) migration and (D) invasion assays, as described in Fig. 1B and C (magnification, ×100). (E) EJ cells were transfected with ctrl siRNA and Wnt5a siRNA for 24 h. After incubation with 4-HPR for 48 h, the protein levels of Wnt5a were measured by western blotting. GAPDH was used as an internal control. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. *P <0.05, **P<0.01 vs. control. 4-HPR, N-(4-hydroxyphenyl) retinamide; siRNA, small interfering RNA; Wnt5a, wingless-type mouse mammary tumor virus integration site family, member 5a; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; C, control; ctrl, control.