FIGURE 3.
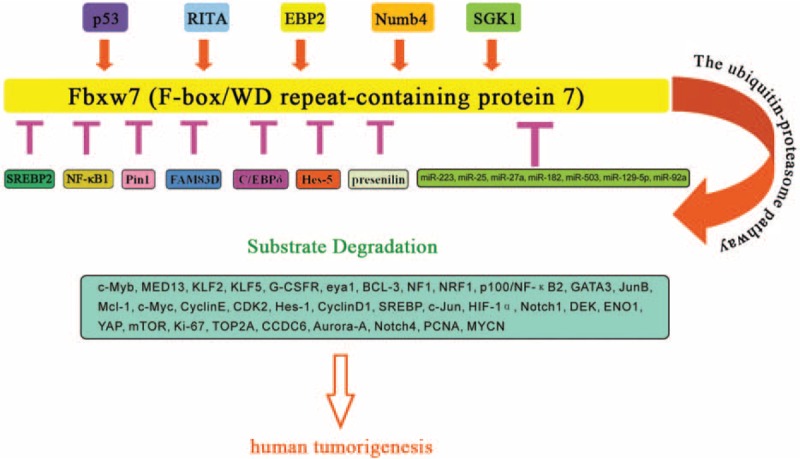
The upstream regulators of Fbxw7 and its major downstream targets that contributes to human tumorigenesis. Fbxw7 coordinates the ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis of several key oncoproteins, such as c-Myb,6 MED13,7 KLF2,8 KLF5,9 G-CSFR,10 eya1,11 BCL-3,12 NF1,13 NRF1,14 p100/NF-κB2,15,16 GATA3,16 JunB,18 Mcl-1,19,20 c-Myc,21–27 CyclinE,21–27 CDK2,16 Hes-1,16 CyclinD1,16 SREBP,28 c-Jun,23,29 HIF-1α,30 Notch1,23,31,32 DEK,23 ENO1,33 YAP,34 mTOR,35,36 Ki-67,24,37 TOP2A,20 CCDC6,38 Aurora-A,26,37,39 Notch4,37 PCNA,37 MYCN,40 and their function linked to defects in cell proliferation, differentiation, genetic instability, and ultimately tumorigenesis. What is more, several proteins such as p53, RITA, EBP2, Numb4, SGK1, SREBP2, NF-κB1, Pin1, FAM83D, C/EBPδ, Hes-5, presenilin, miR-223, miR-25, miR-27a, miR-182, miR-503, miR-129-5p, and miR-92a are found to regulate the expression of Fbxw7. Aurora-A = Aurora kinase A, CCDC6 = coiled-coil-domain containing 6, ENO1 = Enolase 1, Fbxw7 = F-box/WD repeat-containing protein 7, G-CSFR = Granulocyte colony stimulating factor receptor, HIF-1α = Hypoxia inducible factor-1α, KLF2 = Kruppel-like factor 2, KLF5 = Kruppel-like factor 5, Mcl-1 = Myeloid cell leukemia-1, MED13 = Mediator 13, mTOR = mammalian target of rapamycin, NF1 = Neurofibromatosis type 1, NF-κB2 = p100/Nuclear factor-κB2, NRF1 = Nuclear factor E2-related factor 1, PCNA = proliferation cell nuclear antigen, SREBP = sterol regulatory element binding protein, YAP = Yes-associated proteins.
