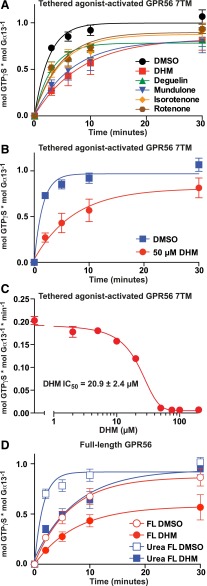
Fig. 3.
Secondary validation assays demonstrating that DHM and other rotenoids inhibit GPR56. (A–C) Prepared membranes containing the full tethered-agonist-activated GPR56 7TM receptor were reconstituted with purified G13 heterotrimer. The kinetics of G13 GTPγS binding were measured in the presence of 50 µM isoflavonoids (DHM, deguelin, mundulone, isorotenone, or rotenone) or DMSO vehicle control (A), or 50 µM DHM or DMSO control with 20 µM GDP present (B). Error bars are the average ± the s.d. of three experimental replicates. (C) The initial rates of full tethered-agonist-activated GPR56 7TM stimulation of G13 GTPγS binding were determined from four point (t = 0,1,2,3 min.) linear functions for each concentration of DHM. The IC50 of DHM inhibition was derived from the semilog plot of a one-phase monoexponential association function using GraphPad Prism. Error bars are the average of each linear line slope (rate) ± the s.d. of three technical replicates. (D) Membranes containing full-length (Karpus et al., 2013) GPR56 receptor were untreated or treated with ice-cold 7 M urea to mimic the proposed process of ligand-mediated receptor activation via N-terminal extracellular fragment dissociation. The kinetics of receptor-activated G13 GTPγS binding were measured in the presence of 50 µM DHM or DMSO control. Error bars were frequently smaller than the plotted symbols and are the average ± the s.d. of three experimental replicates. Full-length FL, full-length.