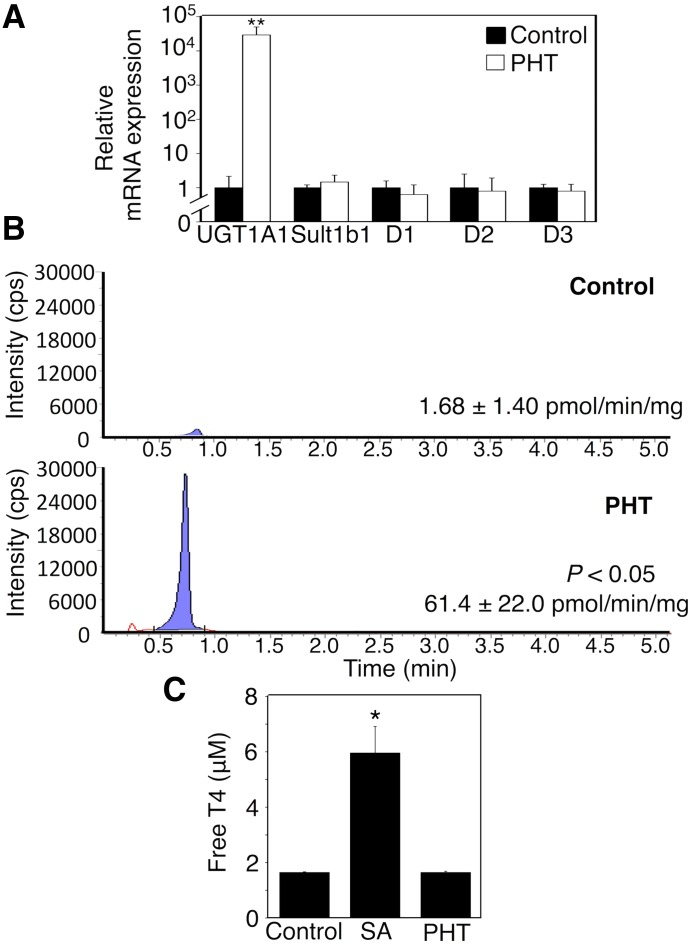
Fig. 1.
Effect of phenytoin treatments during the perinatal period on serum T4 levels and T4 metabolism-related gene expression. Dams and their pups were treated with phenytoin daily from gestation day 12, 13, or 14 to postnatal day 0 (p.o.) and from postnatal day 1 to day 14 (s.c.). (A) Total RNA was prepared from the livers, and mRNA levels of T4-metabolizing enzymes were determined in control mice (closed columns, n = 3) and phenytoin (PHT)-treated mice (open columns, n = 3). Liver microsomes were prepared, and UGT1A1 activity toward T4 was measured. (B) Tandem mass spectrometric chromatograms for T4 glucuronidation in control mice and phenytoin-treated mice are shown. (C) The effect of salicylic acid (SA, n = 3) and phenytoin (n = 3) on T4 binding was determined in vitro. Each column is the mean ± S.D. of biologic replicates. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 compared with control. PHT, phenytoin.