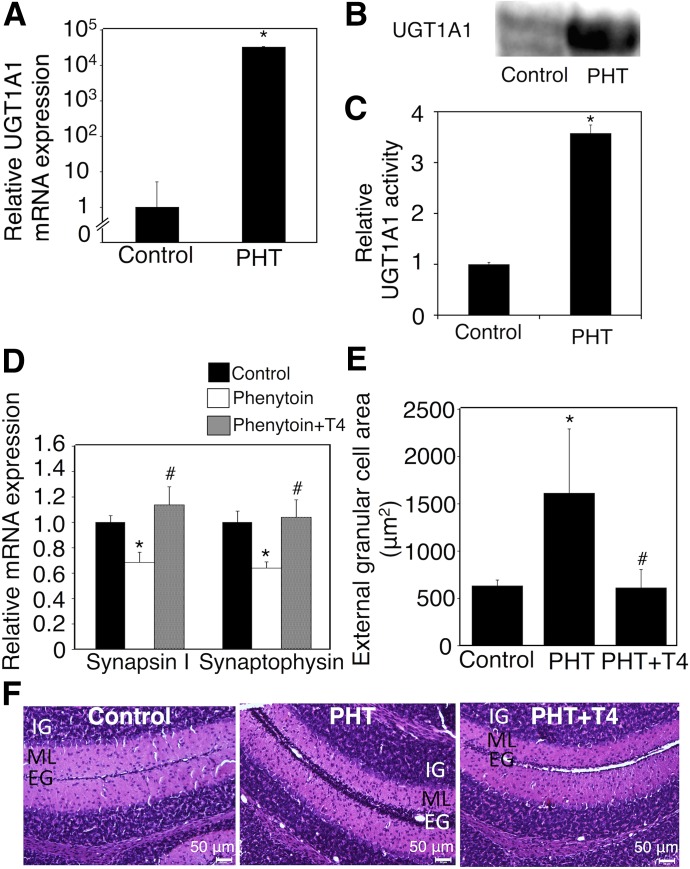
Fig. 4.
Effect of exposure to phenytoin and T4 replacement during the postnatal period on serum free T4 levels and neurodevelopment in hUGT1 mice. Phenytoin (PHT; s.c. 35 mg/kg) was administered to pups daily from postnatal day 1 to day 14 (PHT group). Phenytoin (s.c. 35 mg/kg) and T4 (s.c. 100 μg/kg) were simultaneously administered to pups daily from postnatal day 1 to day 14 (PHT+T4 group). (A) Total RNA was prepared from the livers of control (n = 3) and phenytoin-treated mice (n = 3), and mRNA levels of UGT1A1 were determined. (B) Pooled liver microsomes were prepared from control (n = 3) and phenytoin-treated (n = 2) hUGT1 mice, and western blotting against UGT1A1 was performed. (C) UGT1A1 activity toward estradiol was measured. (D) Total RNA was prepared from the hippocampus, and mRNA levels of synapsin I and synaptophysin were determined in the control group (closed columns, n = 3), PHT group (open columns, n = 3), and PHT+T4 group (gray columns, n = 3). (E) External granule cell area was measured within 50 μm in the horizontal direction of external granule cell layer from randomly selected fields (n = 3). (F) The midsagittal sections of the cerebellum vermis in the control, PHT, and PHT+T4 groups were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Error bars show the S.D. of biologic replicates. *P < 0.05 compared with control group; #P < 0.05 compared with the PHT group. EG, external granule layer; IG, internal granule layer; ML, molecular layer.