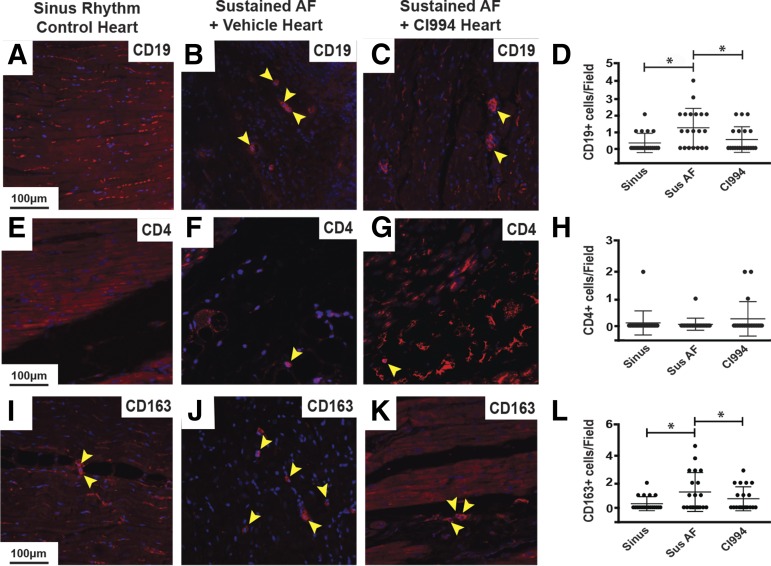
Fig. 4.
CI-994 reduces atrial immune cell infiltration in dogs with sustained AF. Immunostaining of canine left atrial sections with antibodies against CD19 to identify B cells (A–C), CD4 to label helper T cells (E–G), and CD163 to mark macrophages (I–K) from control dogs in sinus rhythm (A, E, and I), dogs with atrial tachypacing-induced sustained AF (B, F, and J), and dogs with sustained AF treated with CI-994 (C, G, and K). Blue staining is 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindol to identify nuclei. Yellow arrowheads point out positively stained cells with stained nuclei. Scale bar in the left-hand panel applies to that row. (D, H, and L) Comparison of the number of CD19+, CD4+, and CD163+ cells per image, respectively. Twenty total images were analyzed from five different hearts/group for each marker. CI-994, sustained atrial fibrillation plus CI-994; Sinus, sinus rhythm; Sus, sustained. *P < 0.05.