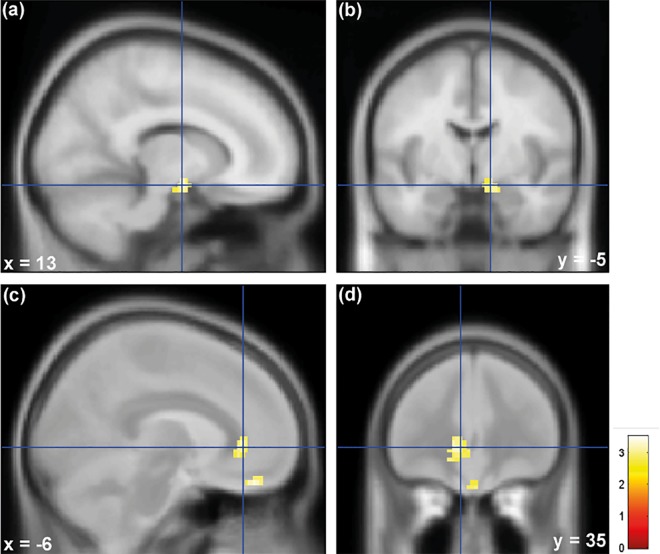
Fig 2.
Shows that Individuals with high neuroticism showed stronger activation in the (a)(b) amygdala and (c)(d) subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (sgACC) when exposed to infant crying compared to individuals with lower neuroticism levels (p < 0.05, FWE small volume corrected). The median (neuroticism score: 1.67) served as the boundary between the high and the low neuroticism groups. A 10 mm radius sphere was placed in sgACC (MNI coordinate: 6/42/-16) and the amygdala (MNI coordinate: 22/-8/-12) based on previous findings that show the involvement of sgACC and amygdala in neuroticism [17]. The results are superimposed on the MNI-152 standard brain (SPM12).