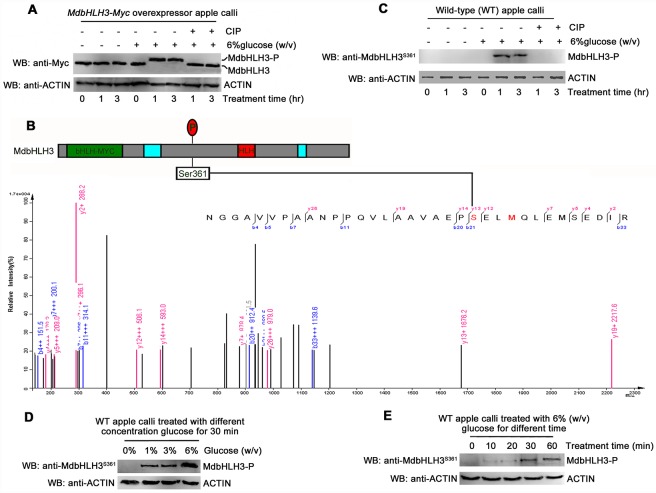
Fig 3. Glucose induces the phosphorylation of the MdbHLH3 protein at the Ser361 site.
(A) Glucose induced the mobility shift of the MdbHLH3 protein, which was abolished by the phosphorylation inhibitor calf intestine alkaline phosphatase (CIP) in the 35S::MdbHLH3-Myc transgenic apple calli. Note: MdbHLH3-P represents phosphorylated MdbHLH3 protein unless noted otherwise in this study. (B) Collision-induced dissociation mass spectrum showing the phosphorylation of Ser-361, a glucose-induced phosphorylation site in MdbHLH3. Top panel: the structural diagram of MdbHLH3 protein and its phosphorylation site. Bottom panel: the phosphorylation sites were identified using LC-MS/MS. MdbHLH3-Myc protein from transgenic apple calli was affinity purified as in (A) before being subjected to in-gel digestion with AspN. (C) Glucose induced the phosphorylation of the MdbHLH3 protein, which was abolished by CIP in WT apple calli. Western blotting was conducted with an anti-MdbHLH3S361 antibody specifically against the phosphorylation site. (D) and (E) The glucose-induced phosphorylation of MdbHLH3 protein depends on glucose concentration (D) and treatment time (E). The WT apple calli was treated with different concentrations of glucose (0, 1%, 3% or 6%) for 30 min (D), or treated with 6% glucose for different times (0, 10, 20, 30, or 60 min) (E). A Western blotting assay was performed with an anti-MdbHLH3S361 antibody.