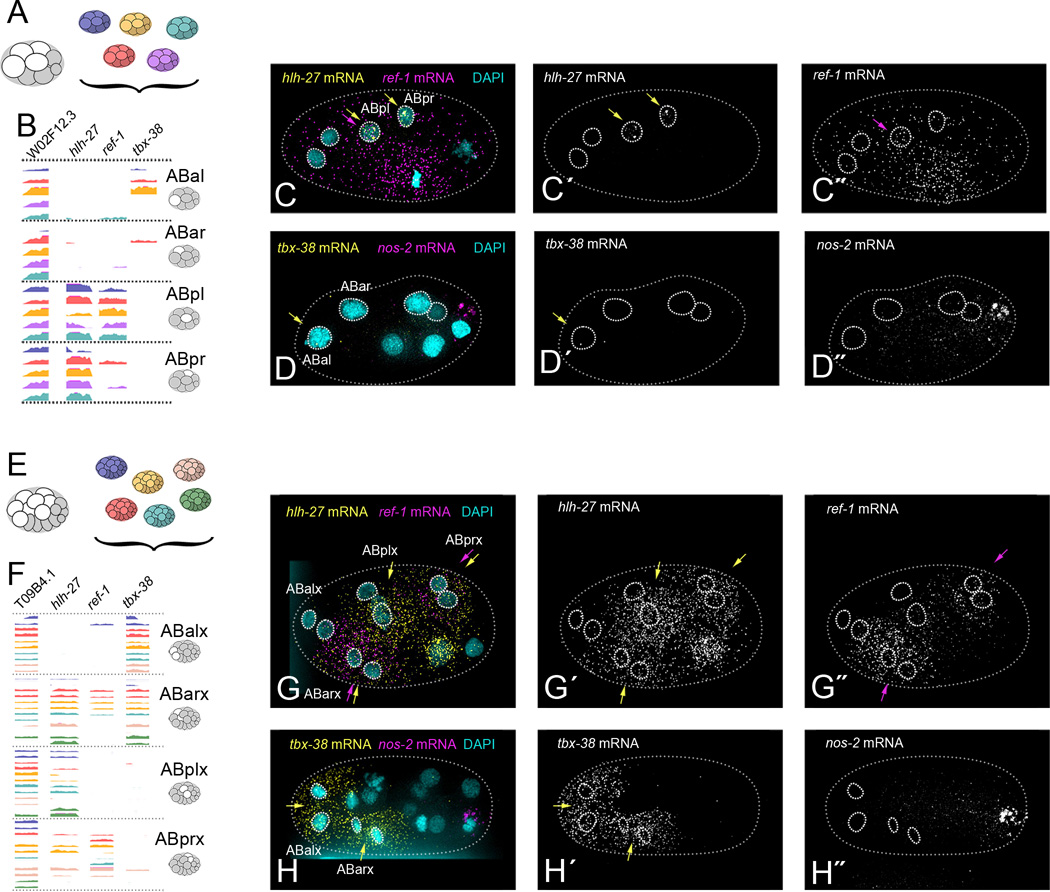
Figure 3. Differential transcript enrichment of notch target genes in cells that could not be distinguished by global transcript signatures.
(A) AB descendants from five replicates of the 8-cell stage embryo.
(B) Genome browser tracks of ABxx transcriptomes, sorted into groups based on expression of notch target genes hlh-27, ref-1 and tbx-38 (Extended Methods). Last exons only are shown.
(C) Example of smFISH targeting hlh-27 (C´, yellow arrows) and ref-1 (C′, purple arrows) transcripts in intact 6- or 8-cell stage embryos (hlh-27 pattern seen in 100% of embryos, n=4. ref-1 pattern seen in 75% of embryos, n=4. Remaining embryo showed ubiquitous ref-1 staining).
(D) Example of smFISH targeting tbx-38 (D´, yellow arrows) in intact 8-cell stage embryos (pattern seen in 33% of embryos, n=3. 67% of embryos showed equal tbx-38 expression in ABal and ABar). (D′) nos-2 (P3-specific) marks the posterior of the embryo.
(E) AB descendants from six replicates of the 16-cell stage embryo.
(F) Genome browser tracks of ABxxx transcriptomes, sorted into four groups based on a PCA using only notch target gene expression (shown in Figure S2D). Last exons only are shown.
(G) Example of smFISH targeting hlh-27 (G´, yellow arrows) and ref-1 (G′, purple arrows) transcripts in intact 15-cell stage embryos (both patterns seen in 100% of embryos, hlh-27 n=5, ref-1 n=2).
(H) Example of smFISH targeting tbx-38 (H´, yellow arrows) in intact 15-cell stage embryos (pattern seen in 100% of embryos, n=14). nos-2 (P4-specific) marks the posterior of the embryo. See Figures S1 and S2 for further identification of ABx, ABxx, and ABxxx transcriptomes.
See also Figure S1, S2