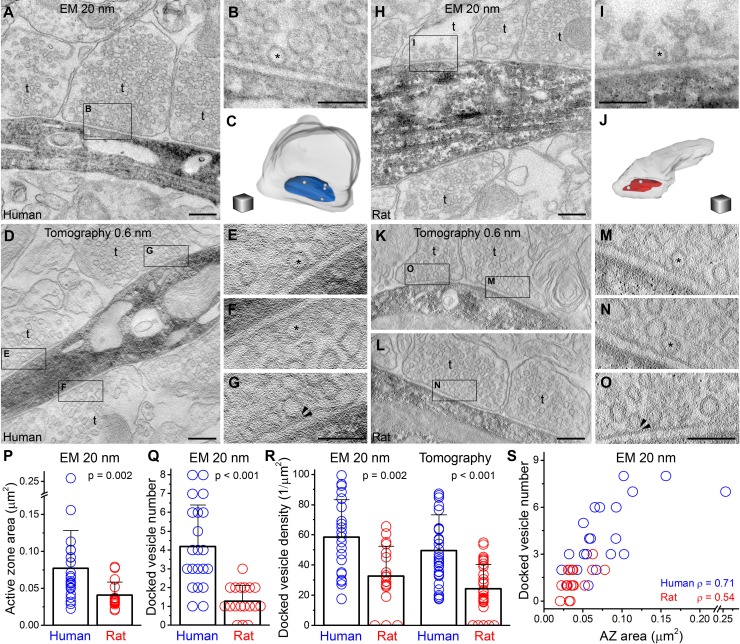
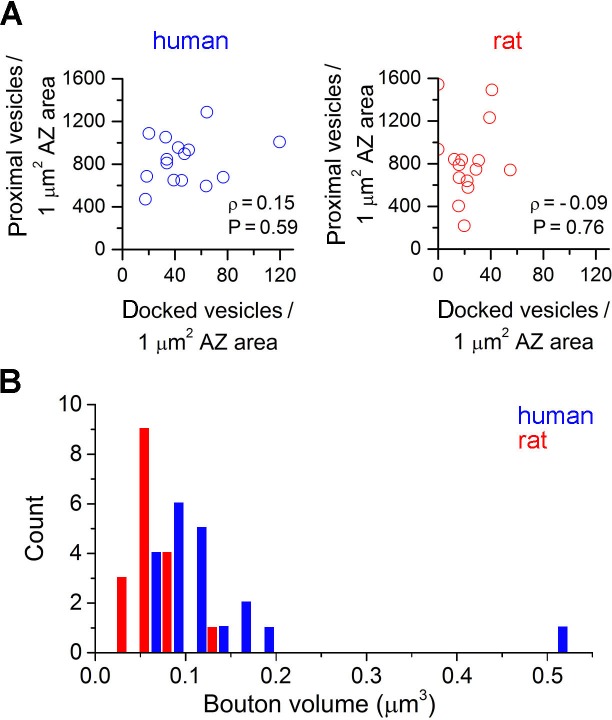
Figure 3. Active zones (AZs) of excitatory synapses are twice as large and harbor 4 times more docked vesicles in human compared to rats.
(A, H) Electron microscopic images of 20 nm thick sections show axon terminals forming asymmetrical synapses on a human (A) and a rat (H) FS cell dendrite (intracellularly filled interneuron visualized with peroxidase: dark precipitate). (B, I) Higher magnification views of the boxed areas in A and H, showing docked vesicles (*) at the AZs. (C, J) 3D reconstructions of the terminals shown in B and I. The human terminal (c, grey semitransparent contour) contains an AZ (blue) of 0.09 μm2 with 4 docked vesicles (white spheres), whereas the rat AZ (red in J) is 0.04 μm2 and has 2 docked vesicles. (D, K–L) Electron tomographic subvolumes (0.6 nm thick) of human (D) and rat (K–L) axon terminals (t) that establish asymmetrical synaptic contacts on FS cell dendrites (dark precipitate). (E–G, M–O) Boxed areas from D and K-L show docked vesicles (*). Panels G and O show membrane proximal vesicles with distances smaller than 5 nm (distance between arrowheads). (P) The area of AZs, determined from 3D reconstructions from 20 nm serial sections, is twice as large in humans than in rats (0.077 ± 0.051 μm2, n = 22, from 3 separate human samples; rat: 0.041 ± 0.017 μm2, n = 19 from 3 animals; p = 0.002, MW U-test). (Q) The number of the docked vesicles, identified in fully reconstructed AZs from 20 nm serial sections, is 4-times larger in human compared to rats (human: 4.2 ± 2.2, n = 21; rat: 1.3 ± 0.8, n = 18, p<0.001, MW U-test). (R) The density of docked vesicles, measured either in 20 nm reconstructions (human: 58.5 ± 24.6 / μm2, n = 21, rat: 32.5 ± 19.9 / μm2, n = 18, p < 0.001, unpaired t-test) or in EM tomographic volumes (human: 49.5 ± 23.8 / μm2, n = 33, rat: 24.3 ± 16.0 / μm2, n = 31, P < 0.001, MW U-test), is significantly different between the two species. (S) The number of the docked vesicles shows a positive correlation with the AZ area (Spearman correlation). Scale bars: A, D, H, K, L: 200 nm, B, E-G, I, M-O: 100 nm, C, J: side of the cubes: 200 nm. Data presented as mean ± SD.