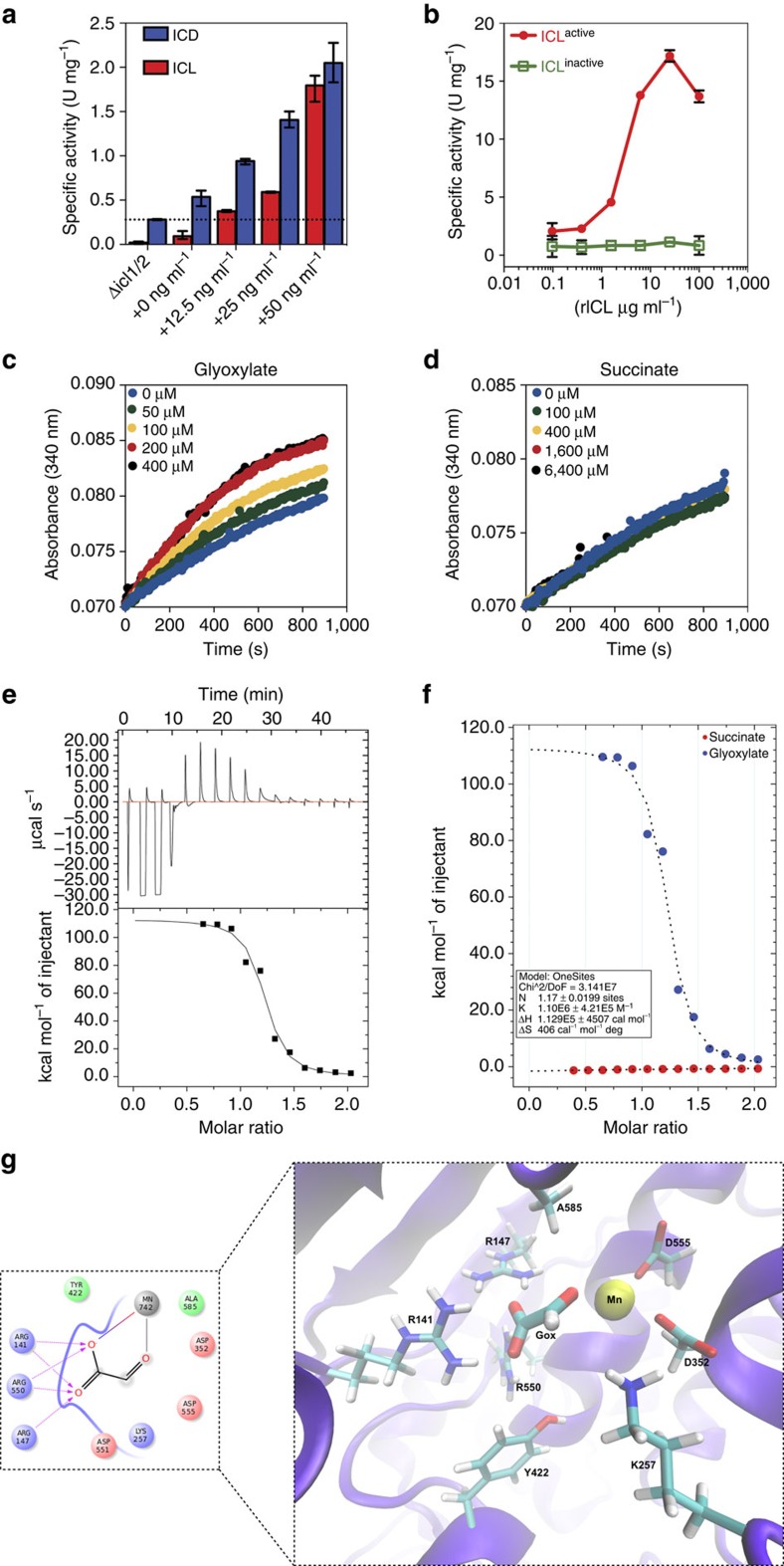
Figure 5. ICD is activated by glyoxylate but not succinate.
(a) ICD activity in vivo increases concomitantly with ICL1 activity in a strain of M. smegmatis that conditionally expresses icl1 from an ATc-inducible promoter. Cells were induced with the indicated concentration of ATc for 18 h before measurement of ICD and ICL1 activities in cell-free extracts. Data are means±s.d. (n=3 independent experiments). (b) rICD activity in vitro is stimulated by active rICL1 in a dose-dependent manner. A catalytically inactive mutant of rICL1 (rICL1KKAGA) does not stimulate ICD activity. (c) rICD activity in vitro is stimulated by glyoxylate in a dose-dependent manner. (d) rICD activity in vitro is not stimulated by succinate. (e) Competitive ITC trace of a solution of glyoxylate-MsmICD binding in 10 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 10 mM EDTA, 50 mM NaCl2 and 2.5 mM MgCl2. Glyoxylate (150 mM) was titrated into MsmICD (15 mM) in the same buffer. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. (f) Kinetics of glyoxylate and succinate interaction with MsmICD. Data was fitted into a single-site binding equation. (g) Detailed view of putative glyoxylate binding site close to the protein active site. Interacting residues Arg147, Arg550, Arg141, Tyr422, Ala585, Asp352, Asp555, Lys257 and Asp551 are shown in stick representation and the magnesium (Mn) as a yellow sphere. (Insert: detailed view of MsmICD–glyoxylate interaction.)